Organizations need to ensure employees, customers and, business partners have appropriate, secure access to information and technology resources. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a central practice for protecting sensitive business data and systems and, the IAM solutions overcome the challenges of IT Security.
Most of the companies are experiencing major data breaches due to poor Identity Access Management Controls.
The lack of identity access management left the largest firms extremely vulnerable. They were primarily guarded by almost every security measure around their data but left the keys in the door. Once inside, the cybercriminals access confidential client emails and documents, including sensitive information of the organization.
Organizations need to ensure employees, customers and, business partners have appropriate, secure access to information and technology resources. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a central practice for protecting sensitive business data and systems and, the IAM solutions overcome the challenges of IT Security.
Most of the companies are experiencing major data breaches due to poor Identity Access Management Controls.
The lack of identity access management left the largest firms extremely vulnerable. They were primarily guarded by almost every security measure around their data but left the keys in the door. Once inside, the cybercriminals access confidential client emails and documents, including sensitive information of the organization.
The necessity of IAM
Security issues are now in a phase where most of the identity methods are no longer sufficient. With the emergence of new technologies, new threats also arise, where IAM helps to significantly mitigate.
Due to the steady growth in areas comprising cloud computing, IT, big data, and BYOD, Security has naturally become a big question as all of these areas depend on it. With an ever-increasing number of threats, data security has always been a major concern.
The IT team must simultaneously meet the needs of a diverse landscape of users across various scenarios including modifications in the access permissions in the on boarding process of new users, current users resignations include sudden terminations and planned retirements, users changing their team a part of their likeliness, promotions, transfers, etc. Due to the amount of information being stored, used, and transmitted, it is necessary to define certain restrictions regarding who is allowed to access the data.
Access to sensitive information should be restricted for users who don’t require it to minimize the risk of data leakage. IAM is not limited to access to a system and sensitive information, the access restrictions can also be applied to internet networks, internet connections, critical websites, access to printers, data centers, software applications, and wireless networks.
Meeting these demands across a variety of on-premises and cloud applications implies the necessity of IAM solutions.
The necessity of IAM
Security issues are now in a phase where most of the identity methods are no longer sufficient. With the emergence of new technologies, new threats also arise, where IAM helps to significantly mitigate.
Due to the steady growth in areas comprising cloud computing, IT, big data, and BYOD, Security has naturally become a big question as all of these areas depend on it. With an ever-increasing number of threats, data security has always been a major concern.
The IT team must simultaneously meet the needs of a diverse landscape of users across various scenarios including modifications in the access permissions in the on boarding process of new users, current users resignations include sudden terminations and planned retirements, users changing their team a part of their likeliness, promotions, transfers, etc. Due to the amount of information being stored, used, and transmitted, it is necessary to define certain restrictions regarding who is allowed to access the data.
Access to sensitive information should be restricted for users who don’t require it to minimize the risk of data leakage. IAM is not limited to access to a system and sensitive information, the access restrictions can also be applied to internet networks, internet connections, critical websites, access to printers, data centers, software applications, and wireless networks.
Meeting these demands across a variety of on-premises and cloud applications implies the necessity of IAM solutions.
Concepts of IAM
- Streamlined Access Management – The user authentication and account management in a single repository either is a physical location or a virtual one. IAM provides confidence that only authorized, authenticated users can interact with the systems and data they need to effectively perform their job roles To work effectively the security professionals managing IAM solutions must understand the business operations as well as the IT systems that enable those operations
- User Provisioning – Creates and manages the user accounts/identity information within the system. The system also will make sure that the users perform actions only within their scope of authority.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) – Authenticating users with a single set of login credentials and providing access to any resources integrated with the SSO portal, which eliminates the need to remember login credentials for each application reduces password reset issues. Basically, the SSO concept in IAM authenticates users once and allowing access to other associated applications.
- Adaptive Authentication – Authentication with Multi-Factor Authentication depends on the users’ risk profile and behavior to balance security requirements with the user experience.
- Multi-Factor Authentication – Authenticating users by multiple authentication factors, e.g., Authenticator App, SMS, Soft/Hard Token, etc. Even if the users lose credentials through a compromise or a device lost, multi-factor authentication (2FA) makes it difficult for attackers to gain access.
- Federated System – Organization follows a common set of standards and procedures for user management. Most of them prefer the federated model since it provides the benefits of a centralized system without putting too many controls in a single system.
- Risk-Based-Authentication – profiling the user attributes to determine the “riskiness” of the authentication and login attempt and adaptively changing the requirements to successfully login. A good example; one can be a legitimate user with valid credentials (username, password and MFA) but you have logged in from a different country whilst you were traveling) – since your geo-location has changed the risk-based authentication profiling will kick-in and validate your identity using different configurable techniques.
Concepts of IAM
- Streamlined Access Management – The user authentication and account management in a single repository either is a physical location or a virtual one. IAM provides confidence that only authorized, authenticated users can interact with the systems and data they need to effectively perform their job roles To work effectively the security professionals managing IAM solutions must understand the business operations as well as the IT systems that enable those operations
- User Provisioning – Creates and manages the user accounts/identity information within the system. The system also will make sure that the users perform actions only within their scope of authority.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) – Authenticating users with a single set of login credentials and providing access to any resources integrated with the SSO portal, which eliminates the need to remember login credentials for each application reduces password reset issues. Basically, the SSO concept in IAM authenticates users once and allowing access to other associated applications.
- Adaptive Authentication – Authentication with Multi-Factor Authentication depends on the users’ risk profile and behavior to balance security requirements with the user experience.
- Multi-Factor Authentication – Authenticating users by multiple authentication factors, e.g., Authenticator App, SMS, Soft/Hard Token, etc. Even if the users lose credentials through a compromise or a device lost, multi-factor authentication (2FA) makes it difficult for attackers to gain access.
- Federated System – Organization follows a common set of standards and procedures for user management. Most of them prefer the federated model since it provides the benefits of a centralized system without putting too many controls in a single system.
- Risk-Based-Authentication – profiling the user attributes to determine the “riskiness” of the authentication and login attempt and adaptively changing the requirements to successfully login. A good example; one can be a legitimate user with valid credentials (username, password and MFA) but you have logged in from a different country whilst you were traveling) – since your geo-location has changed the risk-based authentication profiling will kick-in and validate your identity using different configurable techniques.
How IAM benefits an organization?
IAM solutions facilitate secure and efficient access to technology resources, applications across multiple systems, manage user identities and related access permissions in an automated manner. This brings an organization the following benefits:
- Enhance User Experience: Due to the growth of cloud-based applications employees need to remember the number of passwords for various applications that becomes a challenge for people. Through IAM Single sign-on (SSO) people have an identity that provides access to different systems, external and internal applications, etc., and improves the user experience.
- Improves Business Productivity: The fully Automated provisioning and de-provisioning in IAM speed the implementation of strong security policies and facilitates access to all components of the system which helps to eliminate human error: and reduces delay in the delivery of access results in immediate business productivity.
- Reduced Security Costs: A comprehensive IAM solution helps administrators to consolidate, control, and simplify access privileges for the critical applications that are hosted in traditional data centers, private/public clouds, or a hybrid combination of all these spaces. Utilizing a single IAM platform to manage all user access allows administrators to perform their work more efficiently.
- Improves Data Security: Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables strong authentication to keep your business and brand secure. At the same time, it monitors through analysis, fraud detection and alerts the respective security teams if the activity indicates a possible real risk. A comprehensive, centrally managed IAM solution returns visibility and control over employees’ work practices in a distributed workforce.
- Compliance with Regulations: IAM systems help companies better comply with government regulations by allowing them to show corporate information is not being misused. The IAM solutions can support compliance with regulatory standards including HIPAA, Payment card industry data security standards (PCI DSS) etc. Companies can demonstrate that any data needed for auditing can be made available on demand. IAM also helps to generate the comprehensive reports needed to prove that compliance.
How IAM benefits an organization?
IAM solutions facilitate secure and efficient access to technology resources, applications across multiple systems, manage user identities and related access permissions in an automated manner. This brings an organization the following benefits:
- Enhance User Experience: Due to the growth of cloud-based applications employees need to remember the number of passwords for various applications that becomes a challenge for people. Through IAM Single sign-on (SSO) people have an identity that provides access to different systems, external and internal applications, etc., and improves the user experience.
- Improves Business Productivity: The fully Automated provisioning and de-provisioning in IAM speed the implementation of strong security policies and facilitates access to all components of the system which helps to eliminate human error: and reduces delay in the delivery of access results in immediate business productivity.
- Reduced Security Costs: A comprehensive IAM solution helps administrators to consolidate, control, and simplify access privileges for the critical applications that are hosted in traditional data centers, private/public clouds, or a hybrid combination of all these spaces. Utilizing a single IAM platform to manage all user access allows administrators to perform their work more efficiently.
- Improves Data Security: Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables strong authentication to keep your business and brand secure. At the same time, it monitors through analysis, fraud detection and alerts the respective security teams if the activity indicates a possible real risk. A comprehensive, centrally managed IAM solution returns visibility and control over employees’ work practices in a distributed workforce.
- Compliance with Regulations: IAM systems help companies better comply with government regulations by allowing them to show corporate information is not being misused. The IAM solutions can support compliance with regulatory standards including HIPAA, Payment card industry data security standards (PCI DSS) etc. Companies can demonstrate that any data needed for auditing can be made available on demand. IAM also helps to generate the comprehensive reports needed to prove that compliance.
IAM Framework Development Methodology
Scope of IAM
IAM is no longer just a security tool, it’s an asset that helps to better serve the customers. IAM immensely improves and ensures the businesses to move forward flawlessly and effortlessly.
Using a comprehensive Identity and Access Management system simplifies and automates the process of collecting and controlling employee’s data. If a solution cannot identify its users and assign them the appropriate rights and roles, problems will arise very quickly. IAM ensures compliance with policies and allows administrators/authorized personnel to monitor user behavior and platform service performance.
IAM can be used everywhere due to its encompassing nature, whether on distributed applications, a mobile device, decentralized IT system cloud-based and Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, thus eliminating the barriers for customers to enter the platform anytime, anywhere.
The IAM solutions can ease management pains by enhancing user productivity and can collect and make decisions based on user identity, location, device, and easily revoke or deny privileges to unauthorized users.
The more harmonious the tool fits within the environment and with other security tools, the more likely it is to close security gaps and improve business operations.
IAM Framework Development Methodology
Scope of IAM
IAM is no longer just a security tool, it’s an asset that helps to better serve the customers. IAM immensely improves and ensures the businesses to move forward flawlessly and effortlessly.
Using a comprehensive Identity and Access Management system simplifies and automates the process of collecting and controlling employee’s data. If a solution cannot identify its users and assign them the appropriate rights and roles, problems will arise very quickly. IAM ensures compliance with policies and allows administrators/authorized personnel to monitor user behavior and platform service performance.
IAM can be used everywhere due to its encompassing nature, whether on distributed applications, a mobile device, decentralized IT system cloud-based and Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, thus eliminating the barriers for customers to enter the platform anytime, anywhere.
The IAM solutions can ease management pains by enhancing user productivity and can collect and make decisions based on user identity, location, device, and easily revoke or deny privileges to unauthorized users.
The more harmonious the tool fits within the environment and with other security tools, the more likely it is to close security gaps and improve business operations.
How DTS can help build your IAM Strategy
DTS Solution can help you build your IAM framework which consists of the following phases;
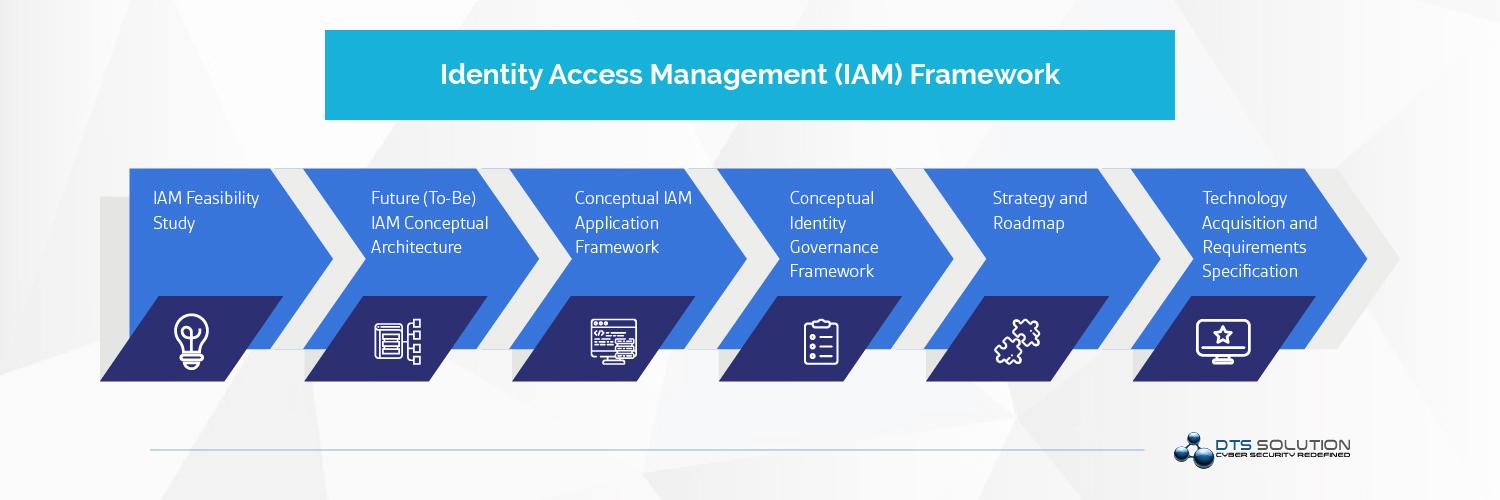
IAM Feasibility Study
- Review critical and business existing applications and services landscape
- Analyze all applications in the current state and integration appetite
- Analyze the nature of users, roles and groups and how these users are managed
- IAM gap assessment and feasibility study report
Conceptual IAM Application Framework
- IAM application integration
- SSO
- SAML
- Federation
- IAM API integration
- IAM cloud integration
- IAM application security
- IAM Plug-Ins
Future To-Be IAM System Architecture
- IAM technical components
- Authentication brokerage
- Context based authentication
- Risk-based authentication
- Application integration
- Centralized Identity store
- 3rd party integration
- Inter-communication
- Authentication and authorization protocols
- Network Security Architecture
- Logging and monitoring
- Active directory integration
- HRMS integration
- Cloud services integration
- Privileged access management
- Strong authentication
- Multi and dual factor authentication
IAM Identity Governance Framework
- Access rights management
- Roles based access control
- Identity access lifecycle workflows
- Application rights management
- Privilege access monitoring
- Accountability and auditability
- Session recording
- Cloud services integration
- Multi-factor authentication
Strategy and Roadmap
- IAM roadmap and strategy
Application integration roadmap Identity lifecycle management Use cases and integrated approach Compliance requirements
Technology Acquisition and Requirements Specification
- Business Requirements Document (BRD)
- Technical Requirements Specification (TRS)
- Compliance Matrix for Technology Evaluation
IAM Feasibility Study
- Review critical and business existing applications and services landscape
- Analyze all applications in the current state and integration appetite
- Analyze the nature of users, roles and groups and how these users are managed
- IAM gap assessment and feasibility study report
Future To-Be IAM System Architecture
- IAM technical components
- Authentication brokerage
- Context based authentication
- Risk-based authentication
- Application integration
- Centralized Identity store
- 3rd party integration
- Inter-communication
- Authentication and authorization protocols
- Network Security Architecture
- Logging and monitoring
- Active directory integration
- HRMS integration
- Cloud services integration
- Privileged access management
- Strong authentication
- Multi and dual factor authentication
Conceptual IAM Application Framework
- IAM application integration
- SSO
- SAML
- Federation
- IAM API integration
- IAM cloud integration
- IAM application security
- IAM Plug-Ins
IAM Identity Governance Framework
- Access rights management
- Roles based access control
- Identity access lifecycle workflows
- Application rights management
- Privilege access monitoring
- Accountability and auditability
- Session recording
- Cloud services integration
- Multi-factor authentication
Strategy and Roadmap
- IAM roadmap and strategy
Application integration roadmap Identity lifecycle management Use cases and integrated approach Compliance requirements
Technology Acquisition and Requirements Specification
- Business Requirements Document (BRD)
- Technical Requirements Specification (TRS)
- Compliance Matrix for Technology Evaluation
See also:
