What's ISO 27002 is all about?
ISO 27002, ISO/IEC 27002 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), formally titled as Information technology – Security techniques – Code of practice for information security controls. It is used as a reference and guidance on the best practices of information security management helping organizations in selecting, implementing, and managing controls.
Why are we discussing ISO 27002 now at this point of time?
The standard used to determine and implement controls for information security management systems to ISO 27001, has been revised and published. The new ISO 27002 edition was released on 15 February 2022.
What are the changes in the ISO 27002: 2022 version?
What's ISO 27002 is all about?
Why are we discussing ISO 27002 now at this point of time?
The standard used to determine and implement controls for information security management systems to ISO 27001, has been revised and published. The new ISO 27002 edition was released on 15 February 2022.
What are the changes in the ISO 27002: 2022 version?

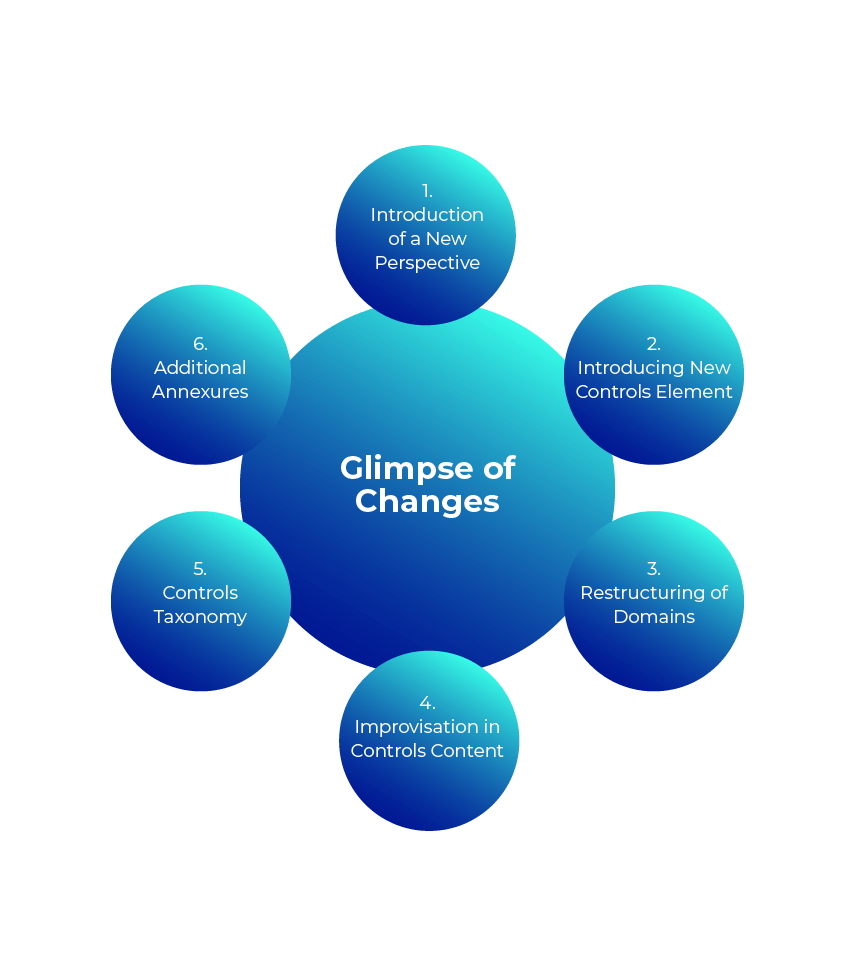
1. Introduction of a New Perspective:
Below are the changes that been adopted in the new update:
1. Change in Approach – The first significant change to the standard is a move away from “Code of Practice” and instead positioning the standard as a set of controls that can either stand alone, or exist as part of an ISO 27001 ISMS.
2. Title Change – The new title is: Information security, Cybersecurity and privacy protection —
Information security controls.
3. Inducing Privacy Protection Angle – Is significant as it supports the privacy information management system ISO 27701 which has increased in popularity as data protection legislation around the world starts to be updated.
2. Introducing New Controls Element:
The structure of control has been changed and the layout for each control contains the following elements:
| New Layout of Controls | Control Title: Short name of the control; |
| Attribute Table: A table showing the attributes for information security of a given control; | |
| Controls: Definition of requirements for a given control; | |
| Purpose: What is the objective of the control and what it should achieve; | |
| Guidance: Considerations for implementing the control; | |
| Other Information: Explanatory text or references to other related documents. |
1. Introduction of a New Perspective:
Below are the changes that been adopted in the new update:
1. Change in Approach – The first significant change to the standard is a move away from “Code of Practice” and instead positioning the standard as a set of controls that can either stand alone, or exist as part of an ISO 27001 ISMS.
2. Title Change – The new title is: Information security, Cybersecurity and privacy protection —
Information security controls.
3. Inducing Privacy Protection Angle – Is significant as it supports the privacy information management system ISO 27701 which has increased in popularity as data protection legislation around the world starts to be updated.
2. Introducing New Controls Element:
The structure of control has been changed and the layout for each control contains the following elements:
| New Layout of Controls | Control Title: Short name of the control; |
| Attribute Table: A table showing the attributes for information security of a given control; | |
| Controls: Definition of requirements for a given control; | |
| Purpose: What is the objective of the control and what it should achieve; | |
| Guidance: Considerations for implementing the control; | |
| Other Information: Explanatory text or references to other related documents. |
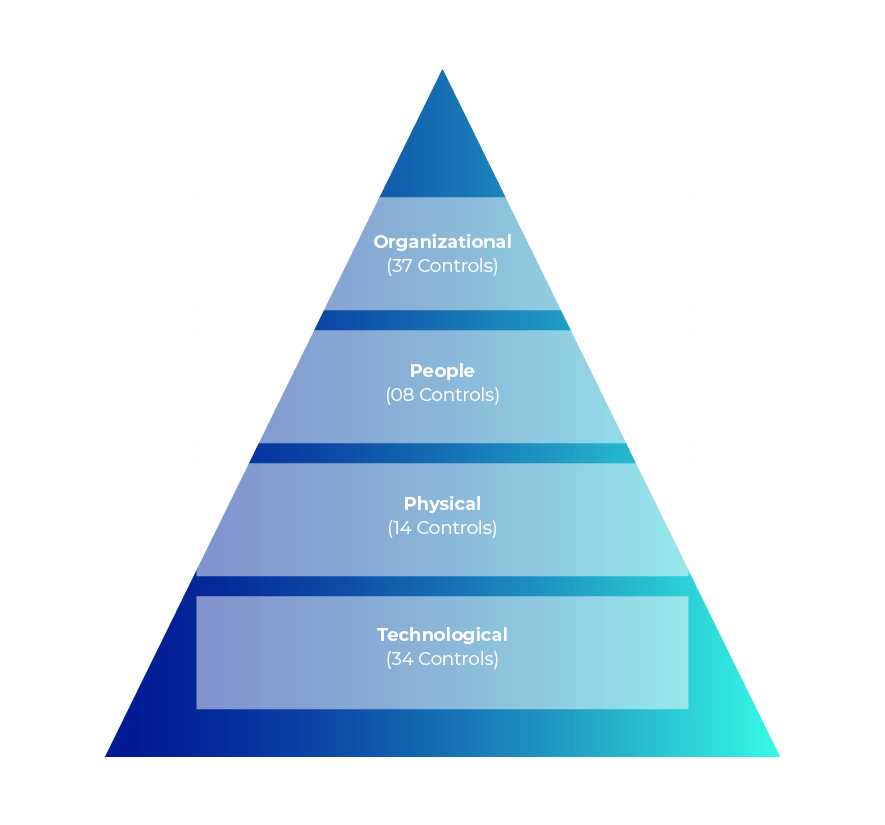
3. Restructuring of Domains:
4. Improvisation in Controls Content:
Like many other changes in the overall layout or structuring of the standard the , we can clearly observe the revision in the content also. Below are the changes in that has been adopted in the new edition:
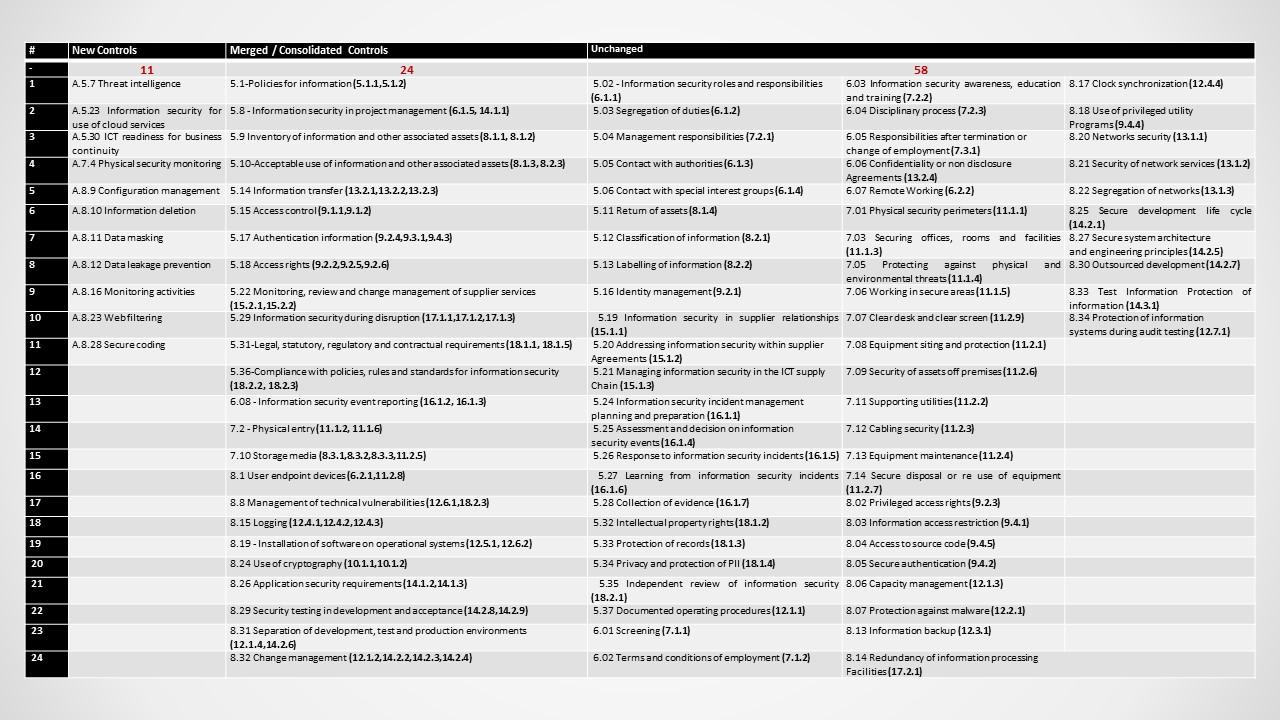
- The control set has been revised down from 114 to 93 controls;
- Many of the controls, 58 of them, remain in place with an update. However the standard has merged 24 controls and
- Added 11 new ones.
Apart from this, Cloud security is one new area that is now covered by the standard, however it should also be noted that the standards committees have given more thought to controls that detect security breaches, in addition to controls that mitigate risks.
Detailed breakdown of controls can be seen in the following image.
3. Restructuring of Domains:

4. Improvisation in Controls Content:
Like many other changes in the overall layout or structuring of the standard the , we can clearly observe the revision in the content also. Below are the changes in that has been adopted in the new edition:
- The control set has been revised down from 114 to 93 controls;
- Many of the controls, 58 of them, remain in place with an update. However the standard has merged 24 controls and
- Added 11 new ones.
Apart from this, Cloud security is one new area that is now covered by the standard, however it should also be noted that the standards committees have given more thought to controls that detect security breaches, in addition to controls that mitigate risks.
Detailed breakdown of controls can be seen in the following image.
5. Controls Taxonomy:
The concept of “attributes to controls” has been introduced, with the intention of enhancing the risk assessment and treatment approach. This will also allow you to create different views—i.e., different categorizations of controls as seen from a different perspective to the control themes. Each control is associated with five attributes with corresponding attribute values (preceded by hashtag “#” [NIST concept] to make them searchable), as follows:
| New Control Taxonomy | Control Type: View from the perspective of when and how the control impacts the risk outcome with regard to the occurrence of an information security incident. Attribute values consist of; #Preventive (the control acts before a threat occurs), #Detective(the control acts when a threat occurs) and, #Corrective(the control acts after a threat occurs). |
| Information Security Properties: View from the perspective of which characteristic of information the control will contribute to preserve. Attribute values consist of : #Confidentiality, #Integrity and #Availability. | |
| Cyber Security Concepts: View from the perspective of the association of controls to Cybersecurity concepts defined in the Cybersecurity framework described in ISO/IEC TS 27101.Attribute values consist of: #Identify, #Protect, #Detect, #Respond and #Recover. | |
| Operational Capabilities: View from the practitioner’s perspective of information security capabilities. Attribute values consist of Security domains: Human_resource_security ; Physical_security ; System_and_network_security ; Application_security ; Secure_configuration Identity_and_access_management ; Threat_and_vulnerability_management ; Continuity; Supplier_relationships_security ; Legal_and_compliance ; Information_security_event_management ; Information_security_assurance ); | |
| Security Domains: View controls from the perspective of information security fields, expertise, services and products. Attribute values consist of #Governance and Ecosystem, #Protection, #Defense and #Resilience |
6. Additional Annexures:
The 2022 version of ISO 27002 includes two very useful annexes which are as follows:
- Annex A– Using attribute:
Annex A explains how an organization can use attributes to create its own views based on the control attributes defined in this document or of its own creation. Basically, it’s a guidance for the application of attributes. - Annex B – Correspondence with ISO/IEC 27002:2013:
Annex B shows the correspondence between the controls in this edition of ISO/IEC 27002 and the previous 2013 edition.
5. Controls Taxonomy:
The concept of “attributes to controls” has been introduced, with the intention of enhancing the risk assessment and treatment approach. This will also allow you to create different views—i.e., different categorizations of controls as seen from a different perspective to the control themes. Each control is associated with five attributes with corresponding attribute values (preceded by hashtag “#” [NIST concept] to make them searchable), as follows:
| New Control Taxonomy |
| Control Type: View from the perspective of when and how the control impacts the risk outcome with regard to the occurrence of an information security incident. Attribute values consist of; #Preventive (the control acts before a threat occurs), #Detective(the control acts when a threat occurs) and, #Corrective(the control acts after a threat occurs). |
| Information Security Properties: View from the perspective of which characteristic of information the control will contribute to preserve. Attribute values consist of : #Confidentiality, #Integrity and #Availability. |
| Cyber Security Concepts: View from the perspective of the association of controls to Cybersecurity concepts defined in the Cybersecurity framework described in ISO/IEC TS 27101.Attribute values consist of: #Identify, #Protect, #Detect, #Respond and #Recover. |
| Operational Capabilities: View from the practitioner’s perspective of information security capabilities. Attribute values consist of Security domains: Human_resource_security ; Physical_security ; System_and_network_security ; Application_security ; Secure_configuration Identity_and_access_management ; Threat_and_vulnerability_management ; Continuity; Supplier_relationships_security ; Legal_and_compliance ; Information_security_event_management ; Information_security_assurance ); |
| Security Domains: View controls from the perspective of information security fields, expertise, services and products. Attribute values consist of #Governance and Ecosystem, #Protection, #Defense and #Resilience |
6. Additional Annexures:
The 2022 version of ISO 27002 includes two very useful annexes which are as follows:
- Annex A– Using attribute:
Annex A explains how an organization can use attributes to create its own views based on the control attributes defined in this document or of its own creation. Basically, it’s a guidance for the application of attributes. - Annex B – Correspondence with ISO/IEC 27002:2013:
Annex B shows the correspondence between the controls in this edition of ISO/IEC 27002 and the previous 2013 edition.
How does ISO 27002:2022 affect ISO 27001?
1
The current version of the ISMS standard remains ISO 27001:2013 (2017) at this time, and therefore the Annex A of this standard remains unchanged, with 114 controls.2
The current ISO Certification schemes will continue on that basis until a revised standard is published.3
It is likely that ISO will publish a revision to ISO 27001 and change ONLY Annex A of that standard by swapping the current control set for the new ISO 27002:2022 set.
How does ISO 27002:2022 affect ISO 27001?
1
The current version of the ISMS standard remains ISO 27001:2013 (2017) at this time, and therefore the Annex A of this standard remains unchanged, with 114 controls.
2
The current ISO Certification schemes will continue on that basis until a revised standard is published.
3
It is likely that ISO will publish a revision to ISO 27001 and change ONLY Annex A of that standard by swapping the current control set for the new ISO 27002:2022 set.
Questions that comes in everybody's mind after this update?
What is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27001 is the standard in which companies gain certification against. Whereas, ISO 27002 is the document that details how to comply with each of the controls in Annex A of ISO 27001.
When are these changes going to take place?
ISO 27002 was updated on February 15, 2022, and Annex A of ISO 27001 will be aligned with those changes. Updates in ISO 27001 Annex A will happen sometime during 2022, the date has not yet been announced.
We want to starting implementing ISO 27001, do we wait until changes are published or should we start now?
For organizations that intend to certify their ISMS, this should not be a showstopper. There is no reason why you cannot start implementing using existing controls and then migrate to the new controls over the next few years once released in ISO 27001.
If we start now with ISO 27001 implementation, do we go with new set of controls or the old ones?
As the changes in ISO 27001 are not published yet, you should start with the existing (old) controls.
Questions that comes in everybody's mind after this update?
What is the difference between ISO 27001 and ISO 27002?
ISO 27001 is the standard in which companies gain certification against. Whereas, ISO 27002 is the document that details how to comply with each of the controls in Annex A of ISO 27001.
When are these changes going to take place?
ISO 27002 was updated on February 15, 2022, and Annex A of ISO 27001 will be aligned with those changes. Updates in ISO 27001 Annex A will happen sometime during 2022, the date has not yet been announced.
We want to starting implementing ISO 27001, do we wait until changes are published or should we start now?
For organizations that intend to certify their ISMS, this should not be a showstopper. There is no reason why you cannot start implementing using existing controls and then migrate to the new controls over the next few years once released in ISO 27001.
If we start now with ISO 27001 implementation, do we go with new set of controls or the old ones?
As the changes in ISO 27001 are not published yet, you should start with the existing (old) controls.
We have already implemented ISO 27001, what do we need to change in our documentation?
To update your risk assessment process with new controls changes in standards are mostly about reorganizing controls, so no changes in technology will be needed, only the changes in the documentation. As the changes are only moderate, our suggestion is that you do not add new documents or delete any of the existing documents. In our opinion, the best way to comply with these changes is:
- To update your risk assessment process with new controls
- To update your Statement of Applicability(SoA)
- To adapt certain sections in your existing policies and procedures.
There are some additional requirements around threat identification , cloud security and cyber security but you may already be compliant with these.
When do we need to change our documentation?
Keep in mind under normal circumstances a publication of a new standard to certify against will have a transition period to allow ISO Certification Bodies and Certified Clients to implement the changes without affecting their certificates. Normally the transition period would be 2 to 3 years depending on where certification is in the current certification cycle. The transition period for these changes is not published yet, but it will most likely be 2 years starting from the date of official ISO 27001:2022 update.
Does the certification body need to check changes in the documentation?
Yes, if your company is certified, the certification body will check if you have adapted your documentation within the transition period. This will take place during your scheduled surveillance audits.
We have already implemented ISO 27001, what do we need to change in our documentation?
To update your risk assessment process with new controls changes in standards are mostly about reorganizing controls, so no changes in technology will be needed, only the changes in the documentation. As the changes are only moderate, our suggestion is that you do not add new documents or delete any of the existing documents. In our opinion, the best way to comply with these changes is:
- To update your risk assessment process with new controls
- To update your Statement of Applicability(SoA)
- To adapt certain sections in your existing policies and procedures.
There are some additional requirements around threat identification , cloud security and cyber security but you may already be compliant with these.
When do we need to change our documentation?
Keep in mind under normal circumstances a publication of a new standard to certify against will have a transition period to allow ISO Certification Bodies and Certified Clients to implement the changes without affecting their certificates. Normally the transition period would be 2 to 3 years depending on where certification is in the current certification cycle. The transition period for these changes is not published yet, but it will most likely be 2 years starting from the date of official ISO 27001:2022 update.
Does the certification body need to check changes in the documentation?
Yes, if your company is certified, the certification body will check if you have adapted your documentation within the transition period. This will take place during your scheduled surveillance audits.