Data is the lifeblood of any organization, especially in this era of cloud computing. However, data also poses significant challenges for cloud security. Data breaches, data leaks, data loss, data corruption, data misuse, and data compliance violations are some common threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud data. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to have a robust and proactive approach to managing and securing their cloud data.
This is where Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) comes in. DSPM is a new paradigm of cloud security that focuses on the data itself rather than the infrastructure or the network.
In this article, we’ll explore DSPM, what it entails, and its role in safeguarding data on the cloud.
Data is the lifeblood of any organization, especially in this era of cloud computing. However, data also poses significant challenges for cloud security. Data breaches, data leaks, data loss, data corruption, data misuse, and data compliance violations are some common threats that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud data. Therefore, it is essential for organizations to have a robust and proactive approach to managing and securing their cloud data.
This is where Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) comes in. DSPM is a new paradigm of cloud security that focuses on the data itself rather than the infrastructure or the network.
In this article, we’ll explore DSPM, what it entails, and its role in safeguarding data on the cloud.
DSPM vs CSPM: What is The Difference?
CSPM is an approach that deals with monitoring and managing the security posture of cloud-based systems and infrastructures. CSPM tools scan the cloud environment for risks and misconfigurations that can expose the organization to threats or violations. CSPM tools also provide recommendations and automation for remediation and prevention of such issues. CSPM tools help organizations comply with various security standards and regulations, such as Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (MCSB), GDPR, HIPAA, NIST, etc. CSPM tools also help organizations optimize their cloud performance and efficiency by eliminating unnecessary or redundant resources.
DSPM is an approach that focuses on discovering, classifying, flow mapping, protecting, monitoring, and remediating the data stored or processed in the cloud and on-premises environments. DSPM tools identify and tag the data based on their sensitivity level and regulatory requirements. DSPM tools also apply granular policies and controls to different categories of data. They help organizations protect their data from unauthorized or malicious access or modification and comply with various data regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc. These tools also help organizations optimize data usage and performance by eliminating obsolete or redundant data.
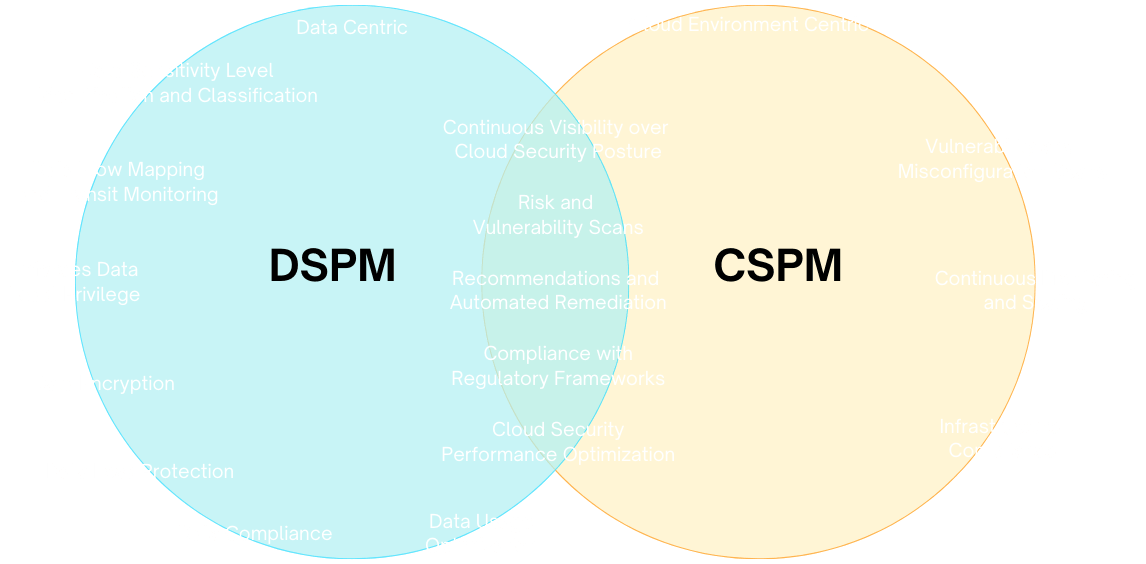
The main difference between CSPM and DSPM is the scope and focus of their security objectives. CSPM aims to secure the cloud infrastructure and services, while DSPM aims to secure the data in the environment. Likewise, CSPM deals with the configuration and compliance of the cloud environment, while DSPM deals with the discovery and protection of the data assets. Also, CSPM helps organizations prevent and mitigate threats at the cloud infrastructure level, while DSPM helps organizations prevent and mitigate threats at the data level.
The main similarity between CSPM and DSPM is that they both provide continuous visibility and control over the cloud security posture. CSPM and DSPM both scan the cloud environment for risks and vulnerabilities and provide recommendations and automation for remediation and prevention. They both help organizations comply with various security standards and regulations that apply to their cloud environment or data assets. Also, they help organizations optimize their cloud security performance and efficiency by eliminating unnecessary or redundant resources or data.
DSPM vs CSPM: What is The Difference?
Cloud security is a complex and dynamic domain that requires multiple layers and dimensions of protection. While DSPM focuses on the data, another approach to security is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM). Let’s have a quick comparison of these two security domains.
CSPM is an approach that deals with monitoring and managing the security posture of cloud-based systems and infrastructures. CSPM tools scan the cloud environment for risks and misconfigurations that can expose the organization to threats or violations. CSPM tools also provide recommendations and automation for remediation and prevention of such issues. CSPM tools help organizations comply with various security standards and regulations, such as Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark (MCSB), GDPR, HIPAA, NIST, etc. CSPM tools also help organizations optimize their cloud performance and efficiency by eliminating unnecessary or redundant resources.
DSPM is an approach that focuses on discovering, classifying, flow mapping, protecting, monitoring, and remediating the data stored or processed in the cloud and on-premises environments. DSPM tools identify and tag the data based on their sensitivity level and regulatory requirements. DSPM tools also apply granular policies and controls to different categories of data. They help organizations protect their data from unauthorized or malicious access or modification and comply with various data regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc. These tools also help organizations optimize data usage and performance by eliminating obsolete or redundant data.
The main difference between CSPM and DSPM is the scope and focus of their security objectives. CSPM aims to secure the cloud infrastructure and services, while DSPM aims to secure the data in the environment. Likewise, CSPM deals with the configuration and compliance of the cloud environment, while DSPM deals with the discovery and protection of the data assets. Also, CSPM helps organizations prevent and mitigate threats at the cloud infrastructure level, while DSPM helps organizations prevent and mitigate threats at the data level.
The main similarity between CSPM and DSPM is that they both provide continuous visibility and control over the cloud security posture. CSPM and DSPM both scan the cloud environment for risks and vulnerabilities and provide recommendations and automation for remediation and prevention. They both help organizations comply with various security standards and regulations that apply to their cloud environment or data assets. Also, they help organizations optimize their cloud security performance and efficiency by eliminating unnecessary or redundant resources or data.

Why Do You Need DSPM?
Data security posture management (DSPM) is not a luxury but a necessity in today’s digital world. As more and more organizations migrate their data to the cloud, they face increasing cyber threats and data breaches that can compromise their data assets and jeopardize their business operations, reputation, and compliance. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach has increased from $3.86 million in 2020 to $4.5 million in 2023—a 15% increase within 3 years. Stats such as this illustrate the need for a more cohesive and efficient approach to cybersecurity.
Why Do You Need DSPM?
Data security posture management (DSPM) is not a luxury but a necessity in today’s digital world. As more and more organizations migrate their data to the cloud, they face increasing cyber threats and data breaches that can compromise their data assets and jeopardize their business operations, reputation, and compliance. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach has increased from $3.86 million in 2020 to $4.5 million in 2023—a 15% increase within 3 years. Stats such as this illustrate the need for a more cohesive and efficient approach to cybersecurity.
Components of DSPM
- Data Discovery and Classification
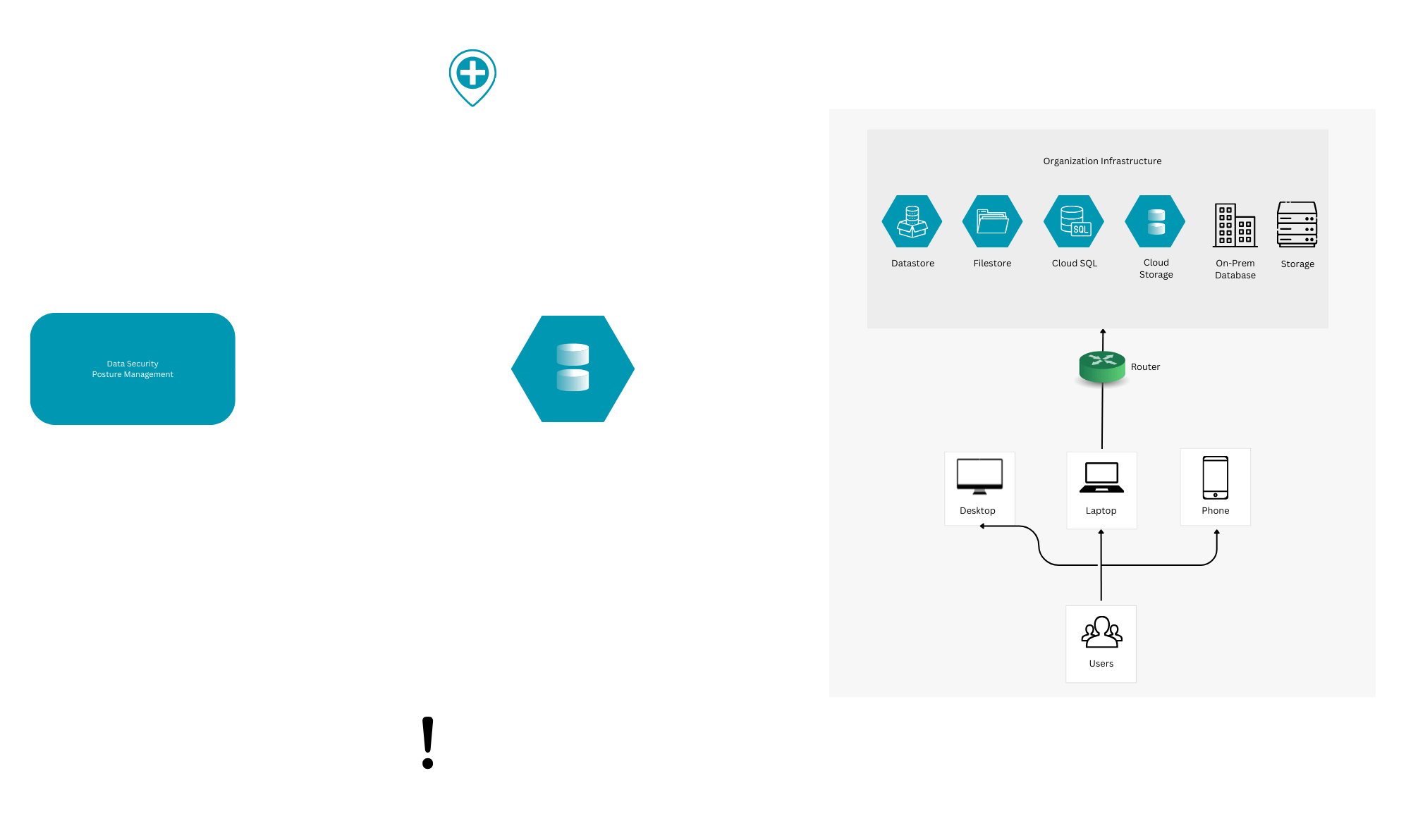
This component involves identifying and cataloging all the data sources and types in the cloud environment, such as cloud storage services, databases, applications, etc. It also involves assigning different sensitivity levels and labels to the data based on their content, context, and regulatory requirements. For example, personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information are considered sensitive data that need higher protection and compliance. Data discovery and classification help organizations understand what kind of data they have, where it is located, how it is used, and how sensitive it is. This enables them to apply appropriate policies and controls to different categories of data and prioritize their security efforts. - Data Flow Mapping
This component involves tracking and visualizing the data flows within and across the cloud environment. It shows how data is accessed, moved, shared, replicated, or deleted by different users, entities, platforms, services, or applications. It also shows the data lineage and provenance, which indicate the origin, history, and ownership of the data. Data flow mapping helps organizations monitor and audit the data activities and transactions in the cloud. It also helps them detect and prevent potential risks and vulnerabilities, such as data leakage, data loss, data corruption, or data misuse.
- Data Risk Management: This component involves assessing and mitigating the related risks and threats that affect the security of the cloud data. It includes performing potential exposed object storage and data stores to performing automated risk assessments to identify and evaluate the security posture of the cloud environment and the data assets.
- Data Incident Detection and Response: This component involves detecting and responding to any security incidents or breaches that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the cloud data. It includes monitoring and alerting on any anomalous or suspicious data access or movement that indicates a potential attack or intrusion. It also includes initiating and executing incident response workflows involving identification, containment, investigation, recovery, and incident reporting. Data incident detection and response help organizations minimize the impact and damage of a data breach and restore their normal operations as soon as possible.
Components of DSPM

A mature DSPM strategy consists of several vital components that work together to provide comprehensive and continuous visibility and control over the data lifecycle in the cloud. These components are:
- Data Discovery and Classification
This component involves identifying and cataloging all the data sources and types in the cloud environment, such as cloud storage services, databases, applications, etc. It also involves assigning different sensitivity levels and labels to the data based on their content, context, and regulatory requirements. For example, personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information are considered sensitive data that need higher protection and compliance. Data discovery and classification help organizations understand what kind of data they have, where it is located, how it is used, and how sensitive it is. This enables them to apply appropriate policies and controls to different categories of data and prioritize their security efforts. - Data Flow Mapping
This component involves tracking and visualizing the data flows within and across the cloud environment. It shows how data is accessed, moved, shared, replicated, or deleted by different users, entities, platforms, services, or applications. It also shows the data lineage and provenance, which indicate the origin, history, and ownership of the data. Data flow mapping helps organizations monitor and audit the data activities and transactions in the cloud. It also helps them detect and prevent potential risks and vulnerabilities, such as data leakage, data loss, data corruption, or data misuse. - Data Risk Management:
This component involves assessing and mitigating the related risks and threats that affect the security of the cloud data. It includes performing potential exposed object storage and data stores to performing automated risk assessments to identify and evaluate the security posture of the cloud environment and the data assets. - Data Incident Detection and Response:
This component involves detecting and responding to any security incidents or breaches that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the cloud data. It includes monitoring and alerting on any anomalous or suspicious data access or movement that indicates a potential attack or intrusion. It also includes initiating and executing incident response workflows involving identification, containment, investigation, recovery, and incident reporting. Data incident detection and response help organizations minimize the impact and damage of a data breach and restore their normal operations as soon as possible.
Applying DSPM for Structured and Unstructured data: The difference
Although not often highlighted in major data protection laws and frameworks, the approach to securing structured and unstructured data can be very different.
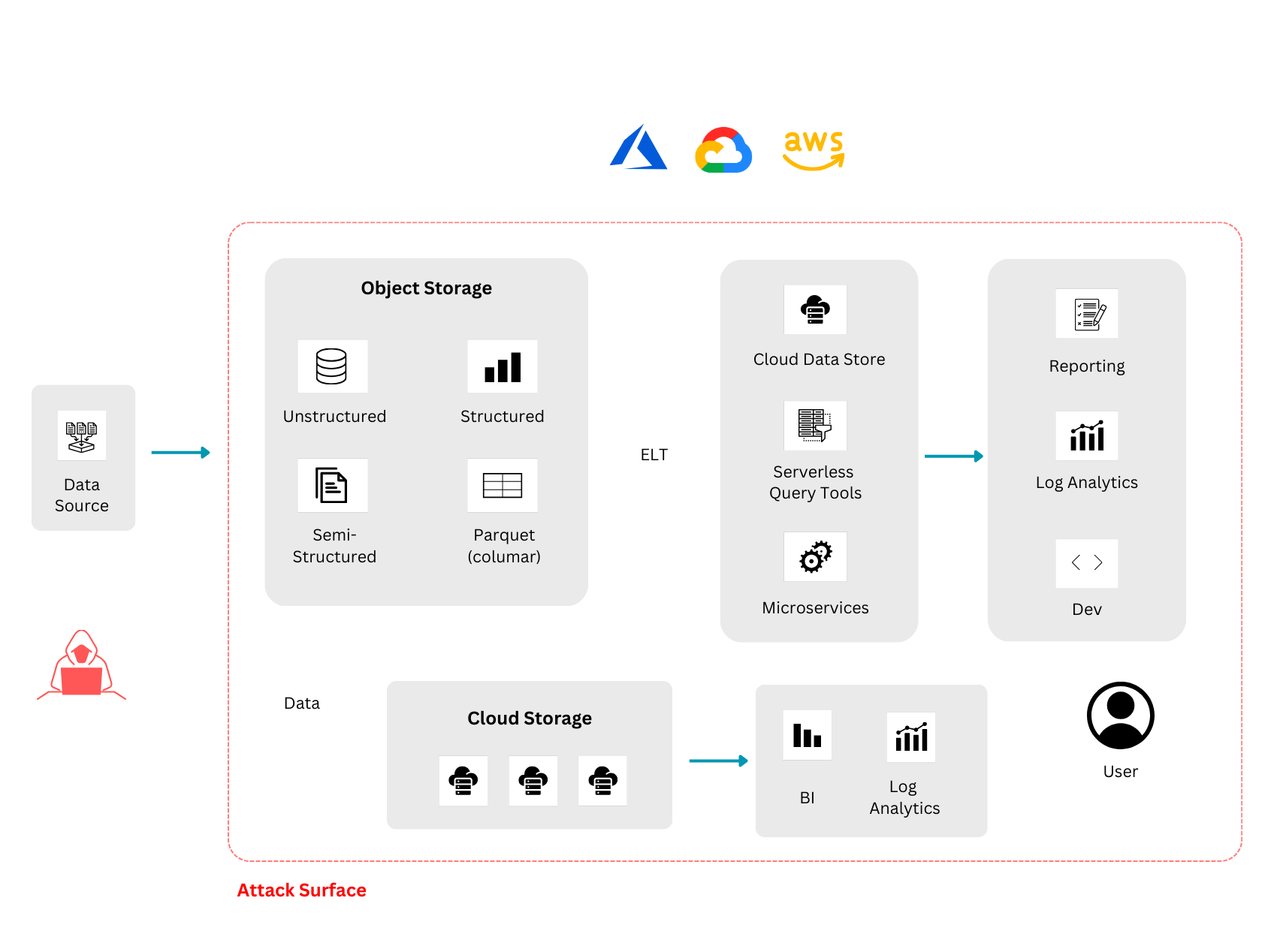
Structured data follows a pre-defined data model and is organized in columns and rows. Such data usually resides in relational databases and can be easily queried and analyzed by machines. Examples of structured data include customer records, product catalogs, sales transactions, etc. In contrast, unstructured data is irregular, and unorganized, and does not follow a pre-defined data model. It usually resides in file systems or data lakes and can be difficult to query and analyze by machines. Some examples of such include emails, videos, images, text files, etc.
DSPM can be applied to both structured and unstructured data, but there are some key differences in how DSPM handles them.
One major difference in unstructured data security is the lack of visibility and control over the data assets. Unstructured data is spread throughout the organization and can be accessed or created by multiple users or entities for various purposes. This makes it hard to know what kind of unstructured data exists, where it is located, how it is used, and how sensitive it is. Moreover, unstructured data can contain personally identifiable information (PII) or other sensitive information that needs to be protected from unauthorized or malicious access or modification.
DSPM helps overcome this challenge by providing comprehensive and continuous visibility and control over the unstructured data lifecycle in the cloud. DSPM enables organizations to:
- Discover and catalog all the unstructured data sources and types in the cloud environment, such as cloud storage services, databases, applications, etc.
- Classify and tag the unstructured data based on their content, context, and regulatory requirements. For example, personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information are considered sensitive data that need higher protection and compliance.
- Protect the unstructured data by applying granular policies and controls based on their sensitivity level and regulatory requirements.
- Monitor and audit the unstructured data activities and transactions in the cloud. For example, who is accessing what data, when, where, why, and how.
- Detect and alert on any anomalous or suspicious unstructured data access or movement that indicates a potential attack or intrusion.
- Remediate any security incidents or breaches that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the unstructured data.
Applying DSPM for Structured and Unstructured data: The difference
Although not often highlighted in major data protection laws and frameworks, the approach to securing structured and unstructured data can be very different.
Structured data follows a pre-defined data model and is organized in columns and rows. Such data usually resides in relational databases and can be easily queried and analyzed by machines. Examples of structured data include customer records, product catalogs, sales transactions, etc. In contrast, unstructured data is irregular, and unorganized, and does not follow a pre-defined data model. It usually resides in file systems or data lakes and can be difficult to query and analyze by machines. Some examples of such include emails, videos, images, text files, etc.
DSPM can be applied to both structured and unstructured data, but there are some key differences in how DSPM handles them.
One major difference in unstructured data security is the lack of visibility and control over the data assets. Unstructured data is spread throughout the organization and can be accessed or created by multiple users or entities for various purposes. This makes it hard to know what kind of unstructured data exists, where it is located, how it is used, and how sensitive it is. Moreover, unstructured data can contain personally identifiable information (PII) or other sensitive information that needs to be protected from unauthorized or malicious access or modification.

DSPM helps overcome this challenge by providing comprehensive and continuous visibility and control over the unstructured data lifecycle in the cloud. DSPM enables organizations to:
- Discover and catalog all the unstructured data sources and types in the cloud environment, such as cloud storage services, databases, applications, etc.
- Classify and tag the unstructured data based on their content, context, and regulatory requirements. For example, personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information are considered sensitive data that need higher protection and compliance.
- Protect the unstructured data by applying granular policies and controls based on their sensitivity level and regulatory requirements.
- Monitor and audit the unstructured data activities and transactions in the cloud. For example, who is accessing what data, when, where, why, and how.
- Detect and alert on any anomalous or suspicious unstructured data access or movement that indicates a potential attack or intrusion.
- Remediate any security incidents or breaches that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the unstructured data.
Conclusion
Conclusion
See also:

