Introduction
You’re probably thinking, “everyday I get on the internet there is a new technology to explore” or you have heard about digital twins and are confused as to what exactly those are.
Forward Networks, a leader in this field, simplifies the definition using Google Maps. With all potential routes and helpful information referenced, Google Maps is a digital replica of the world’s transport network. Again, if you have ever viewed the 3D architectural rendering of a building, you have seen a digital twin.
So what is a digital twin of your network?
You get the picture now. A digital twin is a dynamic and/or real-time digital replica of a physical system, in this case, your network infrastructure.
So a digital twin of any network uses data from sensors and other inputs to mirror the real-world network, allowing you to simulate, analyze, and predict network behavior. It reduces the burdens associated with protecting, updating and maintaining mission-critical network infrastructure.
“Isn’t this as cumbersome as setting up an actual network?”
Good news, advanced solutions now provide powerful tools that help organizations visualize, verify, simulate, and run diagnostics on these replicas. Solution providers create flows and processes that minimize the ambiguity of recreating traditional network architectures. For instance, Forward Networks uses digital twin use cases to tackle identified obstacles and much more by collecting configuration and status information on almost every device in the network, with the ultimate goal of precisely predicting behavior.
Introduction
You’re probably thinking, “everyday I get on the internet there is a new technology to explore” or you have heard about digital twins and are confused as to what exactly those are.
Forward Networks, a leader in this field, simplifies the definition using Google Maps. With all potential routes and helpful information referenced, Google Maps is a digital replica of the world’s transport network. Again, if you have ever viewed the 3D architectural rendering of a building, you have seen a digital twin.
So what is a digital twin of your network?
You get the picture now. A digital twin is a dynamic and/or real-time digital replica of a physical system, in this case, your network infrastructure.
So a digital twin of any network uses data from sensors and other inputs to mirror the real-world network, allowing you to simulate, analyze, and predict network behavior. It reduces the burdens associated with protecting, updating and maintaining mission-critical network infrastructure.
“Isn’t this as cumbersome as setting up an actual network?”
Good news, advanced solutions now provide powerful tools that help organizations visualize, verify, simulate, and run diagnostics on these replicas. Solution providers create flows and processes that minimize the ambiguity of recreating traditional network architectures. For instance, Forward Networks uses digital twin use cases to tackle identified obstacles and much more by collecting configuration and status information on almost every device in the network, with the ultimate goal of precisely predicting behavior.
Now, Picture This
Company A boasts of intricate network infrastructure supporting hundreds of employees, data centers and a myriad of applications until managing it efficiently begins to take a toll on the network operations team, the cybersecurity team and even the application management team.
To keep up with network changes, vendor updates and the growing irritation of employees who use these networks, these teams begin to “cut corners” on best practices. They state that they face the following challenges:
- The network requires regular updates to software, firmware and configurations to stay efficient and secure.
- The infrastructure is made up of devices and software from different vendors, each with an update schedule, policy and of course, compatibility requirements.
- These changes sometimes have complex dependencies meaning that a change in one part of the network can impact many others.
- They HAVE to test and verify these updates and patches.
- Not to mention, the risk of rolling out an update that can inadvertently lead to a downtime, loss of resources (or their jobs).
Now, Picture This
Company A boasts of intricate network infrastructure supporting hundreds of employees, data centers and a myriad of applications until managing it efficiently begins to take a toll on the network operations team, the cybersecurity team and even the application management team. To keep up with network changes, vendor updates and the growing irritation of employees who use these networks, these teams begin to “cut corners” on best practices. They state that they face the following challenges:
- The network requires regular updates to software, firmware and configurations to stay efficient and secure.
- The infrastructure is made up of devices and software from different vendors, each with an update schedule, policy and of course, compatibility requirements.
- These changes sometimes have complex dependencies meaning that a change in one part of the network can impact many others.
- They HAVE to test and verify these updates and patches.
- Not to mention, the risk of rolling out an update that can inadvertently lead to a downtime, loss of resources (or their jobs).
They begin to consider ways to solve these issues without increasing the already robust team of 25 network engineers and 15 cybersecurity experts until someone mentions building a digital twin of their network.
Gartner, in a report released in July, 2023, encouraged I&O leaders to embrace the use of enterprise network digital twins to “reduce risk and chaos”. But why?
The simple answer to this is that a digital twin of any infrastructure can serve as a lab rat providing the following benefits:
- Network Visibility: For any IT/networking professional, not having end-to-end visibility into a network environment is equivalent to flying blind at top speed. Digital twins, according to an IRTF draft report, constantly use mapping and so stay updated about the status of the network and its intricate elements. They provide comprehensive visibility into your entire network which can be used to generate detailed topology maps and path analyses, enabling you to monitor network health, detect anomalies, and quickly identify the root cause of issues.
- Improved Network Design: These replicas are useful to simulate different network configurations and assess their impact on performance using any possible scenario one can think of. This helps in making informed decisions about upgrades and expansions.
- Predictable Network Behaviour: By leveraging simulation and predictive analysis features, you can anticipate potential failures before they occur due to data processing and even AI integration. This proactive approach reduces the risk of downtime and ensures your network runs smoothly.
- Compliance and Security: In contrast to real network data, which is subject to more thorough compliance and privacy regulations, digital twin networks employ large volumes of simulated data. This element may be useful in identifying potential compromise or security flaws.
- Network Training: Probably, one of the major benefits. The ability to test changes or processes in a simulated environment allows network and security personnel to gain expertise with network operations tasks, threat detection, and troubleshooting without the risk of causing a network outage vulnerability or sleepless nights for the C-suite executives.
The benefits are not even limited to being just a “lab rat.”
This technology can aid in cyber remediation, investigation and forensics efforts too. If an organization is faced with an attack, the cybersecurity and IR teams will most often than not first try to gather as much information as possible.
– What devices have been impacted?
– What command-and-control mechanism has been set up?
– What are the servers talking to? Is there a man-in-the-middle?
Use Cases such as Forward Networks’ Blast Radius enable security professionals to get detailed and visual representations of what may have been compromised during the early stages of an attack and even isolate affected or suspicious devices.
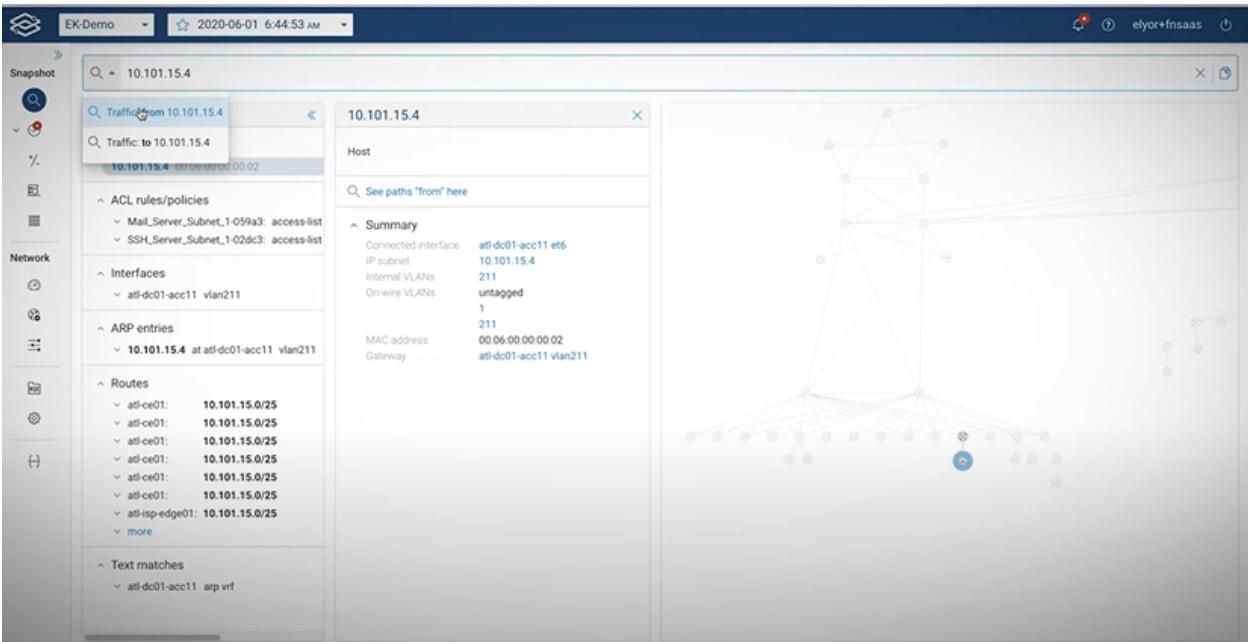
This is a huge feat considering that the behavior of each device would, traditionally, have had to be checked, logged in excel sheets and studied for anomalies before any action is even considered. The Blast Radius model will detail communications to and from any subject IP address, saving precious time and all you need to do is ask (see image below):
They begin to consider ways to solve these issues without increasing the already robust team of 25 network engineers and 15 cybersecurity experts until someone mentions building a digital twin of their network.
Gartner, in a report released in July, 2023, encouraged I&O leaders to embrace the use of enterprise network digital twins to “reduce risk and chaos”. But why?
The simple answer to this is that a digital twin of any infrastructure can serve as a lab rat providing the following benefits:
- Network Visibility: For any IT/networking professional, not having end-to-end visibility into a network environment is equivalent to flying blind at top speed. Digital twins, according to an IRTF draft report, constantly use mapping and so stay updated about the status of the network and its intricate elements. They provide comprehensive visibility into your entire network which can be used to generate detailed topology maps and path analyses, enabling you to monitor network health, detect anomalies, and quickly identify the root cause of issues.
- Improved Network Design: These replicas are useful to simulate different network configurations and assess their impact on performance using any possible scenario one can think of. This helps in making informed decisions about upgrades and expansions.
- Predictable Network Behaviour: By leveraging simulation and predictive analysis features, you can anticipate potential failures before they occur due to data processing and even AI integration. This proactive approach reduces the risk of downtime and ensures your network runs smoothly.
- Compliance and Security: In contrast to real network data, which is subject to more thorough compliance and privacy regulations, digital twin networks employ large volumes of simulated data. This element may be useful in identifying potential compromise or security flaws.
- Network Training: Probably, one of the major benefits. The ability to test changes or processes in a simulated environment allows network and security personnel to gain expertise with network operations tasks, threat detection, and troubleshooting without the risk of causing a network outage vulnerability or sleepless nights for the C-suite executives.
The benefits are not even limited to being just a “lab rat.”
This technology can aid in cyber remediation, investigation and forensics efforts too. If an organization is faced with an attack, the cybersecurity and IR teams will most often than not first try to gather as much information as possible. What devices have been impacted? What command-and-control mechanism has been set up? What are the servers talking to? Is there a man-in-the-middle?
Use Cases such as Forward Networks’ Blast Radius enable security professionals to get detailed and visual representations of what may have been compromised during the early stages of an attack and even isolate affected or suspicious devices.
This is a huge feat considering that the behavior of each device would, traditionally, have had to be checked, logged in excel sheets and studied for anomalies before any action is even considered.
The Blast Radius model will detail communications to and from any subject IP address, saving precious time and all you need to do is ask (see image below):

Within seconds, you can run search filters leveraging all possible destination IPs, ports, MAC addresses etc that have interacted with the subject of your investigation. An analyst’s heaven.
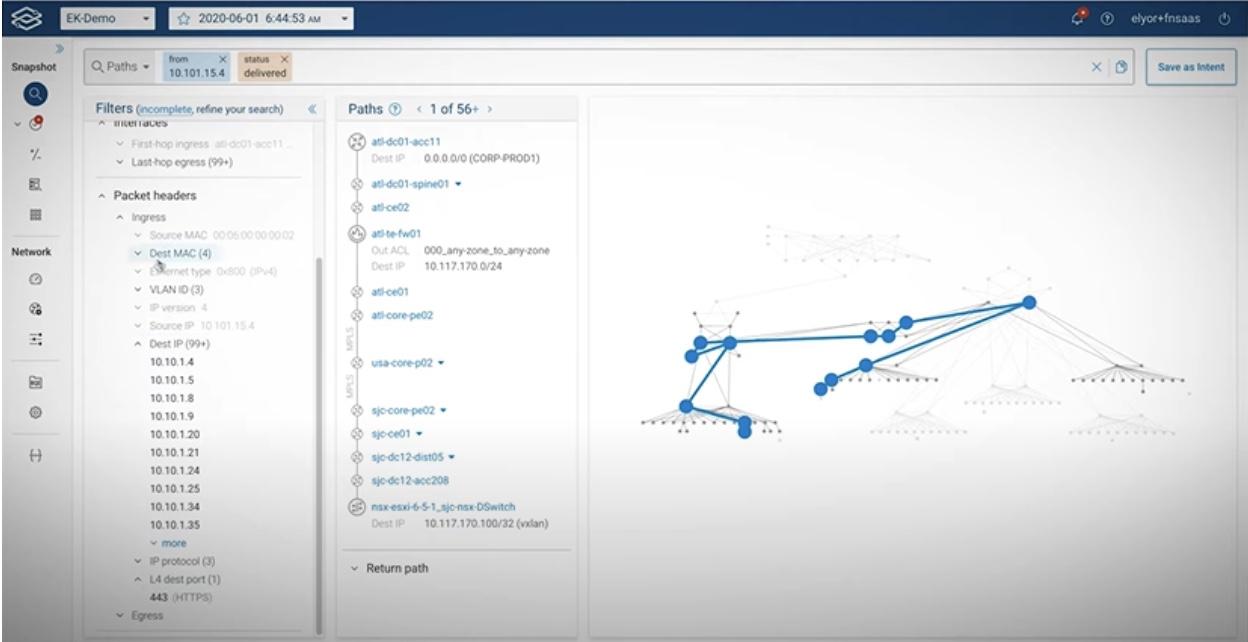
It is also useful in risk analysis as it can reveal all possible ways to access critical infrastructure and what best ways to harden security. This powerful feature may just have discovered the anomalies in network traffic which plagued the 2019 SolarWinds supply chain attack that lasted well over 14 months, you know, saved precious time and revealed, with mathematical accuracy, where hackers were lurking.
Within seconds, you can run search filters leveraging all possible destination IPs, ports, MAC addresses etc that have interacted with the subject of your investigation. An analyst’s heaven.

It is also useful in risk analysis as it can reveal all possible ways to access critical infrastructure and what best ways to harden security.
This powerful feature may just have discovered the anomalies in network traffic which plagued the 2019 SolarWinds supply chain attack that lasted well over 14 months, you know, saved precious time and revealed, with mathematical accuracy, where hackers were lurking.
Building a Digital Twin
Now that the benefits have been presented, how does an organization create this technology, you may ask. Regardless of what organization provides a solution, proper considerations must be made and steps followed in order to avoid further ambiguity as network topologies are already a hassle to navigate. These include:
Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
Start by clearly defining what you aim to achieve with your digital twin. Determine the scope of the twin—whether it will cover the entire network or focus on specific components.
Step 2: Gather Data
Collect data from your network infrastructure. This includes static data such as network topology and configuration, as well as dynamic data like traffic patterns and performance metrics. Advanced network solutions facilitate this with robust data collection capabilities.
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools
Select the appropriate platform for creating and managing your digital twin. It should provide comprehensive tools for network simulation, monitoring, and even AI-driven analytics.
The following are some essential tools and technologies to consider when building your digital twin:
| Tool/Technology | Description |
| Network Visualization | Detailed topology maps and path analyses. |
| Verification Engine | Ensures network configurations match the intended state. |
| Simulation Tools | Simulates network changes and predicts their impact. |
| Automated Diagnostics | Identifies and troubleshoots network issues automatically. |
| AI Analytics | Provides predictive maintenance and optimization insights |
Step 4: Create the Digital Twin Model
Develop the digital model of your network using the collected data. The platform will help create an accurate virtual representation of network nodes, connections, and devices.
Step 5: Integrate Real-Time Data
Incorporate real-time data feeds into your digital twin to ensure it accurately reflects the current state of your network. The platform should support seamless integration via APIs and sensors.
Step 6: Validate and Test
Validate the accuracy of your digital twin by comparing its behavior with the actual network. Conduct tests, also, using simulation tools to ensure it performs as expected under various scenarios.
Step 7: Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Regularly update your digital twin with new data and insights. Use the platform for continuous monitoring, simulation, and optimization of your network infrastructure.
Integrating this into existing businesses processes will not be a walk in the park but a few tips to ensure seamless adoption include:
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project focusing on a specific segment of your network.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Accurate data is crucial for an effective digital twin.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Involve network engineers, IT staff, and data scientists in the project.
- Leverage Automation: Use automation tools to keep the digital twin updated with minimal manual intervention.
- Regularly Review and Update: Continuously refine the digital twin based on new data and insights.
Building a Digital Twin
Now that the benefits have been presented, how does an organization create this technology, you may ask. Regardless of what organization provides a solution, proper considerations must be made and steps followed in order to avoid further ambiguity as network topologies are already a hassle to navigate. These include:
Step 1: Define Objectives and Scope
Start by clearly defining what you aim to achieve with your digital twin. Determine the scope of the twin—whether it will cover the entire network or focus on specific components.
Step 2: Gather Data
Collect data from your network infrastructure. This includes static data such as network topology and configuration, as well as dynamic data like traffic patterns and performance metrics. Advanced network solutions facilitate this with robust data collection capabilities.
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools
Select the appropriate platform for creating and managing your digital twin. It should provide comprehensive tools for network simulation, monitoring, and even AI-driven analytics. The following are some essential tools and technologies to consider when building your digital twin:
| Tool/Technology | Description |
| Network Visualization | Detailed topology maps and path analyses. |
| Verification Engine | Ensures network configurations match the intended state. |
| Simulation Tools | Simulates network changes and predicts their impact. |
| Automated Diagnostics | Identifies and troubleshoots network issues automatically. |
| AI Analytics | Provides predictive maintenance and optimization insights |
Step 4: Create the Digital Twin Model
Develop the digital model of your network using the collected data. The platform will help create an accurate virtual representation of network nodes, connections, and devices.
Step 5: Integrate Real-Time Data
Incorporate real-time data feeds into your digital twin to ensure it accurately reflects the current state of your network. The platform should support seamless integration via APIs and sensors.
Step 6: Validate and Test
Validate the accuracy of your digital twin by comparing its behavior with the actual network. Conduct tests, also, using simulation tools to ensure it performs as expected under various scenarios.
Step 7: Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Regularly update your digital twin with new data and insights. Use the platform for continuous monitoring, simulation, and optimization of your network infrastructure.
Integrating this into existing businesses processes will not be a walk in the park but a few tips to ensure seamless adoption include:
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project focusing on a specific segment of your network.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Accurate data is crucial for an effective digital twin.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Involve network engineers, IT staff, and data scientists in the project.
- Leverage Automation: Use automation tools to keep the digital twin updated with minimal manual intervention.
- Regularly Review and Update: Continuously refine the digital twin based on new data and insights.
Finally…
If you are Company A or even smarter, creating the digital replica of your network is embracing the future. Based on findings reported by Gartner and IRTF, almost every IT/networking professional in organizations is faced with properly dealing with the growing complexity of their networks, issues surrounding vendor compatibility, functionality of devices and architecture and even cost optimization. This technology offers you the capability of predicting and modifying network changes without affecting critical business processes and infrastructure.
Listen to Guruprasad Ramamoorthy explain how this technology delivers a seamless network experience.
And if you still have doubts, – “It is an emerging technology that will change the way enterprises roll out network changes” – take Gartner’s words for it.
Finally
If you are Company A or even smarter, creating the digital replica of your network is embracing the future. Based on findings reported by Gartner and IRTF, almost every IT/networking professional in organizations is faced with properly dealing with the growing complexity of their networks, issues surrounding vendor compatibility, functionality of devices and architecture and even cost optimization. This technology offers you the capability of predicting and modifying network changes without affecting critical business processes and infrastructure.
Listen to Guruprasad Ramamoorthy explain how this technology delivers a seamless network experience.
And if you still have doubts, – “It is an emerging technology that will change the way enterprises roll out network changes” – take Gartner’s words for it.
See also:

