Introduction
-
PasswordState Password Manager Provider
A software update to Click Studios' Passwordstate password manager contained malware -
HashiCorp Open-Source Software Tools and Infrastructure Provider
Victim of Codecov supply-chain attack -
Rapid7 Cyber Security Tools and Solutions Provider
Rapid7 source code, alert data accessed in Codecov supply-chain attack
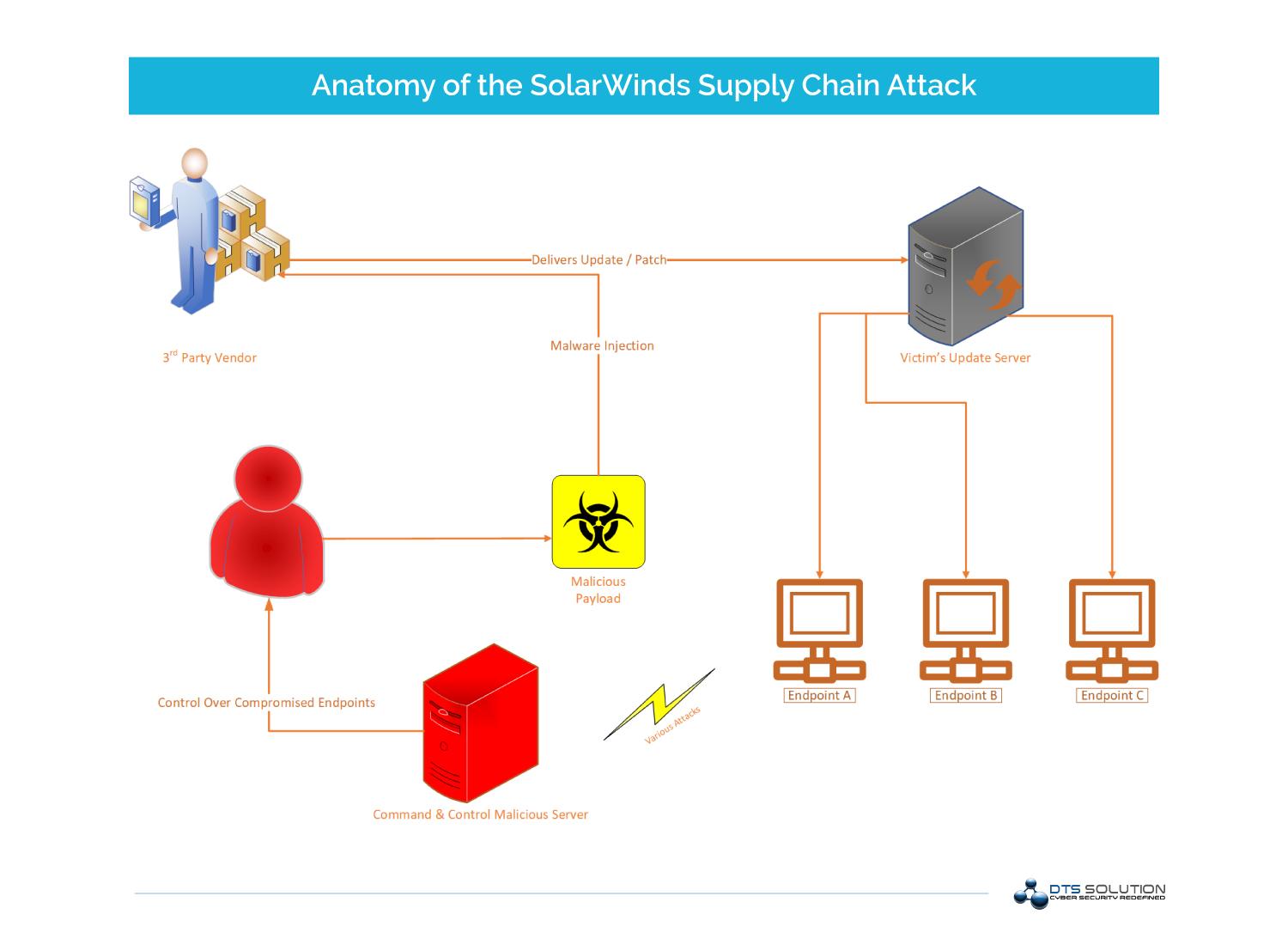
SolarWinds is a company that develops a network and applications monitoring platform called Orion, which attackers used to their advantage by distributing Trojan updates to the clients’ organizations that were using the Orion software. This attack is one of the dozens that have occurred in cybersecurity global attacks history that is attributed to supply-chain attacks. By hackers targeting software developers and vendors they are able to compromise many organization by injecting malicious payloads into source code and binaries of software that are then used by their customers. Resulting in a cascading effect of breaches.
Introduction
-
PasswordState Password Manager Provider
A software update to Click Studios' Passwordstate password manager contained malware -
HashiCorp Open-Source Software Tools and Infrastructure Provider
Victim of Codecov supply-chain attack -
Rapid7 Cyber Security Tools and Solutions Provider
Rapid7 source code, alert data accessed in Codecov supply-chain attack
SolarWinds is a company that develops a network and applications monitoring platform called Orion, which attackers used to their advantage by distributing Trojan updates to the clients’ organizations that were using the Orion software. This attack is one of the dozens that have occurred in cybersecurity global attacks history that is attributed to supply-chain attacks. By hackers targeting software developers and vendors they are able to compromise many organization by injecting malicious payloads into source code and binaries of software that are then used by their customers. Resulting in a cascading effect of breaches.
Anatomy of the SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
- Site to site IPSEC VPN connection to third party outsourced service provider
- Remote Access (SSL VPN) from third party support personal to your environment
- Untrusted or semi-trusted B2B partner connection through WAN / MPLS
- Use of third party software for core business services
- Contractor / third party connecting into your corporate environment
- Adoption of a SaaS or other cloud services
- Use of outsourced data or transaction processing organization
The possible threat scenarios stemming from your supply-chain is pretty endless.
Anatomy of the SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
- Site to site IPSEC VPN connection to third party outsourced service provider
- Remote Access (SSL VPN) from third party support personal to your environment
- Untrusted or semi-trusted B2B partner connection through WAN / MPLS
- Use of third party software for core business services
- Contractor / third party connecting into your corporate environment
- Adoption of a SaaS or other cloud services
- Use of outsourced data or transaction processing organization
The possible threat scenarios stemming from your supply-chain is pretty endless.
Cyber Risks that may derive from Outsourced Third Parties
-
Data Exfiltration
Suppose a successful compromise of third party vendor update delivery method and product that is supposed to be deployed on the client-side via third party platform, website, etc. In that case, an attacker may successfully modify the payload and delivery malware that can compromise the endpoint. If we assume that the attackers' objective is to steal that, they may very well be able to do that. -
Privilege Abuse
It is no secret that most of the third parties have logical privileges on the clients' organization's infrastructure. The reason may vary for that, starting from remote connectivity and maintenance, ending with configuration update and hardening from the vendor. It is common to see that client-side organization does not perform privilege access management and this will allow the malicious actor to have the ability to abuse the privilege and cause destruction.
-
Intelligence Gathering
The attacker that has managed to compromise even a low-level privilege still gives the ability to gather intelligence about the critical infrastructure of the organization, such as the number of endpoints, what kind of endpoints are installed (OS version, software installed, etc.) via third party compromised accounts that have certain privileges. -
Physical Destruction
An organization running critical operational infrastructures such as water plants, nuclear plants, or any other industrial OT infrastructure can be under significant destructive risk because state-sponsored advanced attackers usually compromise critical industrial systems via third parties. After all, the OT environments are usually heavily secured. -
Unintended Human Mistake
Inadvertent mistakes subcontractor's employees can cause just as much damage as intentional attacks. Common mistakes include accidentally deleting or sharing files and information, inputting incorrect data, and misconfiguring systems and solutions. These mistakes can still lead to data leaks, service outages, and significant revenue losses while unintentional.
Cyber Risks that may derive from Outsourced Third Parties
-
Data Exfiltration
Suppose a successful compromise of third party vendor update delivery method and product that is supposed to be deployed on the client-side via third party platform, website, etc. In that case, an attacker may successfully modify the payload and delivery malware that can compromise the endpoint. If we assume that the attackers' objective is to steal that, they may very well be able to do that. -
Privilege Abuse
It is no secret that most of the third parties have logical privileges on the clients' organization's infrastructure. The reason may vary for that, starting from remote connectivity and maintenance, ending with configuration update and hardening from the vendor. It is common to see that client-side organization does not perform privilege access management and this will allow the malicious actor to have the ability to abuse the privilege and cause destruction.
-
Intelligence Gathering
The attacker that has managed to compromise even a low-level privilege still gives the ability to gather intelligence about the critical infrastructure of the organization, such as the number of endpoints, what kind of endpoints are installed (OS version, software installed, etc.) via third party compromised accounts that have certain privileges. -
Physical Destruction
An organization running critical operational infrastructures such as water plants, nuclear plants, or any other industrial OT infrastructure can be under significant destructive risk because state-sponsored advanced attackers usually compromise critical industrial systems via third parties. After all, the OT environments are usually heavily secured. -
Unintended Human Mistake
Inadvertent mistakes subcontractor's employees can cause just as much damage as intentional attacks. Common mistakes include accidentally deleting or sharing files and information, inputting incorrect data, and misconfiguring systems and solutions. These mistakes can still lead to data leaks, service outages, and significant revenue losses while unintentional.
Conducting Third-Party Security Assurance
- Overview - Privilege management is one of the pillars of having mature and secure infrastructure because all infrastructure activities are done via privileges. Only centralized management of these privileges will provide the ability to grant or deny the privileges properly by monitoring the activities performed and detecting all privileges used by various users, which will provide the ability to detect privilege abuse attack discussed in "Threats and Risk That May Derive from third Parties" section above.
- Remediation - It is highly recommended to deploy a Privilege Access Management (PAM) solution within your environment, which will provide the platform of centralized privilege management.
- Overview - Third parties usually establish remote connectivity to the client's organization infrastructure to perform various services and activities, common and ordinary. Still, it is crucial to secure this connectivity as well as to put strict security control in place to ensure that users that try to establish remote connectivity are authorized to as well as endpoint compliance must be ensured to verify that host that attempts to connect is malware-free, because the infection may spread to other hosts
- Remediation -The following control is highly recommended to be deployed and integrated with to enhance the cyber resilience against supply-chain attacks:
- Multi-factor authentication enforcement on remote connectivity from third party
- Endpoint Compliance Host check Solution
- Instead of allowing direct connection to critical endpoints within your infrastructure, deploy a bastion host that will provide connectivity to endpoints
- Enabling monitoring functionality – SIEM with specific third-party monitoring use cases
- Overview - Network security is another pillar of cyber resilience as it stands for the security of overall network infrastructure and internal connectivity between the zones. It is vital to perform best network hardening practices to eliminate the chance of malware spreading via supply-chain attack and eliminate the possibility of allowing the attacker that derives from third party to perform lateral movement within the network.
- Remediation -The following control is highly recommended to be deployed and integrated with to enhance the cyber resilience against supply-chain attacks:
- Proper network segmentation and segregation according to criticality and similarity of the service or asset
- Internal firewalls deployment and default gateway configuration to be set to the firewall with solid policies and rules to control the traffic between network zone
- Overview - Organization does not have a right to manage the infrastructure and security controls of third party vendors; hence we must put our focus more into enhancing our castle rather than others, but an organization can create a cybersecurity questionnaire and assess the cyber maturity of the third party vendor to understand what kind of risk vectors exist and how to remediate them.
- Remediation - Develop third party questionnaires and assess the infrastructure and security controls of the vendor. Below are given some examples of questions that can be asked to the third party:
- Does the third party share the confidential data of the client with other organizations (4th party)?
- Does the third party perform application penetration testing to ensure that the supplied application or software is not vulnerable?
- Does the third party perform software composition analyses to ensure that the software uses non-vulnerable library dependencies?
- Many mor.
Conducting Third-Party Security Assurance
- Overview - Privilege management is one of the pillars of having mature and secure infrastructure because all infrastructure activities are done via privileges. Only centralized management of these privileges will provide the ability to grant or deny the privileges properly by monitoring the activities performed and detecting all privileges used by various users, which will provide the ability to detect privilege abuse attack discussed in "Threats and Risk That May Derive from third Parties" section above.
- Remediation - It is highly recommended to deploy a Privilege Access Management (PAM) solution within your environment, which will provide the platform of centralized privilege management.
- Overview - Network security is another pillar of cyber resilience as it stands for the security of overall network infrastructure and internal connectivity between the zones. It is vital to perform best network hardening practices to eliminate the chance of malware spreading via supply-chain attack and eliminate the possibility of allowing the attacker that derives from third party to perform lateral movement within the network.
- Remediation -The following controls and practices are highly recommended to be performed to ensure cyber resilience against supply-chain attacks:
- Proper network segmentation and segregation according to criticality and similarity of the service or asset
- Internal firewalls deployment and default gateway configuration to be set to the firewall with solid policies and rules to control the traffic between network zone.
- Overview - Third parties usually establish remote connectivity to the client's organization infrastructure to perform various services and activities, common and ordinary. Still, it is crucial to secure this connectivity as well as to put strict security control in place to ensure that users that try to establish remote connectivity are authorized to as well as endpoint compliance must be ensured to verify that host that attempts to connect is malware-free, because the infection may spread to other hosts
- Remediation -The following control is highly recommended to be deployed and integrated with to enhance the cyber resilience against supply-chain attacks:
- Multi-factor authentication enforcement on remote connectivity from third party
- Endpoint Compliance Host check Solution
- Instead of allowing direct connection to critical endpoints within your infrastructure, deploy a bastion host that will provide connectivity to endpoints
- Enabling monitoring functionality – SIEM with specific third-party monitoring use cases
- Overview - Organization does not have a right to manage the infrastructure and security controls of third party vendors; hence we must put our focus more into enhancing our castle rather than others, but an organization can create a cybersecurity questionnaire and assess the cyber maturity of the third party vendor to understand what kind of risk vectors exist and how to remediate them.
- Remediation - Develop third party questionnaires and assess the infrastructure and security controls of the vendor. Below are given some examples of questions that can be asked to the third party:
- Does the third party share the confidential data of the client with other organizations (4th party)?
- Does the third party perform application penetration testing to ensure that the supplied application or software is not vulnerable?
- Does the third party perform software composition analyses to ensure that the software uses non-vulnerable library dependencies?
- Many mor.
See also: