- About Us
-
-
- About UsWe are the regional leaders in cybersecurity. We are masters in our tradecraft. We are dynamic, talented, customer-centric, laser-focused and our mission is to defend and protect our customers from cyber adversaries through advisory, consulting, engineering, and operational services.
-
-
- Solutions
-
-
- SolutionsThe cybersecurity industry is fragmented. We have carefully curated an interoperable suite of cybersecurity products and solutions that focus on improving your security compliance and risk maturity that add real business value, effectiveness, and ROI. Combined with our professional services and security engineering expertise we design, architect, implement and operate complex environments and protect your digital space.
-
- Industry
-
-
- IndustryCyber adversaries and threat actors have no boundaries. No industry is immune to cyber-attacks. Each industry has unique attributes and requirements. At DTS we have served all industry verticals since inception and have built specialization in each segment; to ensure our customers can operate with a high degree of confidence and assurance giving them a competitive advantage.
-
- Services
-
-
- ServicesOur cybersecurity services are unmatched in the region. With our unique customer-centric approach and methodology of SSORR we provide end-to-end strategic and tactical services in cybersecurity. We on-ramp, develop, nurture, build, enhance, operationalize, inject confidence, and empower our customers.
-
-
- Vendors
- Products
- Resources
- Press Center
- Tweets
- Support
- Contact
-
Red Teaming Exercises
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
This exercise enables us to provide a realistic analysis of how breaches occur while providing valuable insight into the business and mission impact of network intrusions.
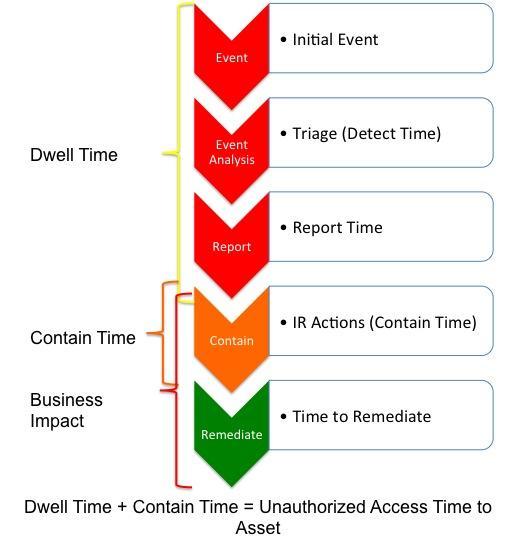
- Were you able to detect the attack?
- How long did it take to detect it?
- How long did it take to respond to the attack?
- Was the response the correct one?
| Ref | Scenario | Description of Testing Scenario | Objectives |
|
External Threat Vector – Cyber Attacker |
|||
| 1 | Malicious outsider attacking the external facing applications and infrastructure of the organization | A threat actor performing application and network based penetration testing to obtain unauthorized access to your organizations online published applications or obtain remote code execution or remote access;
|
All published online applications on the Internet should be subject to application penetration testing across primary and secondary data centers. By performing application-based penetration testing you will benefit from understanding our current security state and posture related to application security, security SDLC and Source Code Review processes whilst ensuring Application Security remains an important priority for business continuity. Application Security is usually the area with little attention due to time to market constraints on custom and purpose-built applications. |
| 2 | Malicious outsider attacking the external boundaries of the organizational logical and physical perimeter | A threat actor attempting to penetrate the corporate infrastructure through network penetration and social engineering techniques through physical means:
|
All types of social engineer techniques related to network access intrusion will be performed to validate the resiliency of processes amongst the different team (service desk, branch location and physical security guards, office cleaners etc.). The activity will be performed like a malicious threat actor with intent of gaining unauthorized internal corporate network access. |
| 3 | Malicious outsider attacking the external facing applications and infrastructure of the organization | A threat actor performing a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack regarding external IP addresses owned by the organization.
|
A simulated drill for DDoS will ensure the processes and procedures in the incident of a DDoS attack are being followed – roles and responsibilities are defined along with mitigation and countermeasure techniques between the service owners and DDoS Mitigation Provider. The Mean Time To Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Response (MTTR) should be evaluated and benchmarked against known KPI and SLA for DDoS Attack Vector. |
| 4 | Malicious outsider creating a zero-day malware to circumvent perimeter email security controls to infiltrate corporate endpoints | A threat actor developing a zero-day malware exploit with the objective to circumvent advanced perimeter security controls (advanced malware for web and email) to take RCE (remote code execution) of endpoints to infiltrate data;
|
The purpose of this test is to validate the security configuration and resiliency of advanced evasive malware detection tools deployed within your organization. The exercise will help in understanding the preparedness level against targeted evasive malware attacks directed towards your environment. The exercise will also test the processes of malware infection and remediation on endpoints. |
|
Internal Threat Vector – Employee / Trusted |
|||
| 5 | Malicious Insider to exploit and gain elevated privileged access to obtain confidential information | An insider threat actor trying to exploit weak system, network and application configuration regarding business applications or sensitive data repositories / data bases.
|
This activity will provide a complete security posture view of critical business applications from an insider threat perspective. A simulated penetration test with valid normal user account will be used to see what elevated privileges access can be achieved and if confidential data can be retrieved. |
| 6 | Malicious Insider performing Electronic Data Theft | An insider threat actor performing Electronic Data Theft;
|
By performing this exercise, you will know the overall resiliency and ability to catch data exfiltration and theft attempts. The exercise will also test security operations center capabilities in detecting such exfiltration attempts with subsequent actions that should be performed. |
| 7 | Malicious Insider performing Physical Data Theft | An insider threat actor performing Physical Data Theft;
|
This exercise will validate the resiliency against physical data theft whilst ensuring that processes related to physical theft are known and executed in a timely manner. |
| 8 | Malicious Insider abusing user access privilege. | Privilege Abuse: A user performs an action that they should not have, according to organizational policy or regulations.
Privileged Account and User Monitoring (PAUM) is a very important exercise to perform. A set of simulated scenarios will be performed but not limited to the below;
|
This exercise will validate the effectiveness against security operations and monitoring controls against PAUM internal threat actors. 90% of cyber threats materializing are due to successful exploitation of abuse of privileged accounts. |
|
External Threat Vector – Customer / Supplier |
|||
| 9 | Malicious Customer / Supplier Exploiting Vulnerabilities against Online Applications | An external threat actor who is an authorized customer or supplier exploiting vulnerabilities within your online applications for fraudulent objectives;
|
|
|
External Threat Vector – Semi-Trusted 3rd Party |
|||
| 10 | Compromised or Malicious Third Party (Semi-Trusted) entity connecting into your organizatiopn | Exploitation of a compromised Third Party who has Network Access to your systems / applications by performing a Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Test across the different transport medium;
|
This exercise will mimic a malicious or compromised semi-trusted third party connecting to your environment. This exercise will validate the security process of third party interconnection and how open or stringent the security controls are in place for 3rd party interconnectivity. |
| 11 | Malicious Third Party (Semi-Trusted) user connecting into your network infrastructure | Insider Malicious Third-Party Staff who has network access to your environment – see scenarios above which cover this test criteria. | This scenario would test the ability for your organization to identify unknown and non-corporate devices on the network once connected. How well the NAC security policies are applied and how the network segmentation is applied for 3rd party endpoints connecting into your corporate network. |
|
Social Engineering |
|||
| 14 | Hacker gaining access to internal confidential information through Social Engineering techniques | External threat actor performing all types of social engineering techniques;
|
This process will validate how effective and efficient your internal infrastructure (people process and technology) is when it comes to Social Engineering attacks and the level of cyber security awareness across your employees. |
- Were you able to detect the attack?
- How long did it take to detect it?
- How long did it take to respond to the attack?
- Was the response the correct one?
| Ref | Scenario | Description of Testing Scenario | Objectives |
External Threat Vector – Cyber Attacker | |||
| 1 | Malicious outsider attacking the external facing applications and infrastructure of the organization | A threat actor performing application and network based penetration testing to obtain unauthorized access to your organizations online published applications or obtain remote code execution or remote access;
| All published online applications on the Internet should be subject to application penetration testing across primary and secondary data centers.
By performing application-based penetration testing you will benefit from understanding our current security state and posture related to application security, security SDLC and Source Code Review processes whilst ensuring Application Security remains an important priority for business continuity. Application Security is usually the area with little attention due to time to market constraints on custom and purpose-built applications. |
| 2 | Malicious outsider attacking the external boundaries of the organizational logical and physical perimeter | A threat actor attempting to penetrate the corporate infrastructure through network penetration and social engineering techniques through physical means:
|
All types of social engineer techniques related to network access intrusion will be performed to validate the resiliency of processes amongst the different team (service desk, branch location and physical security guards, office cleaners etc.).
The activity will be performed like a malicious threat actor with intent of gaining unauthorized internal corporate network access.
|
| 3 | Malicious outsider attacking the external facing applications and infrastructure of the organization | A threat actor performing a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack regarding external IP addresses owned by the organization.
DDoS attack should be simulated based on pre-approved internal memo without notification to monitoring NOC and SOC team. The simulation can also happen during off-peak traffic flow and minimal user transactions. | A simulated drill for DDoS will ensure the processes and procedures in the incident of a DDoS attack are being followed – roles and responsibilities are defined along with mitigation and countermeasure techniques between the service owners and DDoS Mitigation Provider. The Mean Time To Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Response (MTTR) should be evaluated and benchmarked against known KPI and SLA for DDoS Attack Vector. |
| 4 | Malicious outsider creating a zero-day malware to circumvent perimeter email security controls to infiltrate corporate endpoints
| A threat actor developing a zero-day malware exploit with the objective to circumvent advanced perimeter security controls (advanced malware for web and email) to take RCE (remote code execution) of endpoints to infiltrate data;
| The purpose of this test is to validate the security configuration and resiliency of advanced evasive malware detection tools deployed within your organization.
The exercise will help in understanding the preparedness level against targeted evasive malware attacks directed towards your environment. The exercise will also test the processes of malware infection and remediation on endpoints. |
Internal Threat Vector – Employee / Trusted | |||
| 5 | Malicious Insider to exploit and gain elevated privileged access to obtain confidential information | An insider threat actor trying to exploit weak system, network and application configuration regarding business applications or sensitive data repositories / data bases.
The above list is not complete and should be based on the Business Service Catalog. |
This activity will provide a complete security posture view of critical business applications from an insider threat perspective. A simulated penetration test with valid normal user account will be used to see what elevated privileges access can be achieved and if confidential data can be retrieved.
|
| 6 | Malicious Insider performing Electronic Data Theft | An insider threat actor performing Electronic Data Theft;
A simulated attack will be performed where we will obtain a desktop / laptop with limited privileges with all the expected security controls in place. Malicious insider will aim to circumvent corporate controls to perform data theft – however any attempt performed by the red team should be identified and monitored by the security operations center. |
By performing this exercise, you will know the overall resiliency and ability to catch data exfiltration and theft attempts.
The exercise will also test security operations center capabilities in detecting such exfiltration attempts with subsequent actions that should be performed.
|
| 7 | Malicious Insider performing Physical Data Theft | An insider threat actor performing Physical Data Theft;
| This exercise will validate the resiliency against physical data theft whilst ensuring that processes related to physical theft are known and executed in a timely manner. |
| 8 | Malicious Insider abusing user access privilege. | Privilege Abuse: A user performs an action that they should not have, according to organizational policy or regulations. Privileged Account and User Monitoring (PAUM) is a very important exercise to perform. A set of simulated scenarios will be performed but not limited to the below;
The above is just a few examples – a complete set of testing scenarios for PAUM will be developed to validate again. | This exercise will validate the effectiveness against security operations and monitoring controls against PAUM internal threat actors.
90% of cyber threats materializing are due to successful exploitation of abuse of privileged accounts. |
External Threat Vector – Customer / Supplier | |||
| 9 | Malicious Customer / Supplier Exploiting Vulnerabilities against Online Applications | An external threat actor who is an authorized customer or supplier exploiting vulnerabilities within your online applications for fraudulent objectives;
| |
External Threat Vector – Semi-Trusted 3rd Party | |||
| 10 | Compromised or Malicious Third Party (Semi-Trusted) entity connecting into your organizatiopn | Exploitation of a compromised Third Party who has Network Access to your systems / applications by performing a Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Test across the different transport medium;
|
This exercise will mimic a malicious or compromised semi-trusted third party connecting to your environment. This exercise will validate the security process of third party interconnection and how open or stringent the security controls are in place for 3rd party interconnectivity. |
| 11 | Malicious Third Party (Semi-Trusted) user connecting into your network infrastructure | Insider Malicious Third-Party Staff who has network access to your environment – see scenarios above which cover this test criteria. | This scenario would test the ability for your organization to identify unknown and non-corporate devices on the network once connected. How well the NAC security policies are applied and how the network segmentation is applied for 3rd party endpoints connecting into your corporate network. |
Social Engineering | |||
| 14 | Hacker gaining access to internal confidential information through Social Engineering techniques | External threat actor performing all types of social engineering techniques;
| This process will validate how effective and efficient your internal infrastructure (people process and technology) is when it comes to Social Engineering attacks and the level of cyber security awareness across your employees. |
Solutions
Network and Infrastructure Security
Zero Trust and Private Access
Endpoint and Server Protection
Vulnerability and Patch Management
Data Protection
Application Security
Secure Software and DevSecOps
Cloud Security
Identity Access Governance
Governance, Risk and Compliance
Security Intelligence Operations
Incident Response
Accreditations


Accreditations


Dubai
Office 7, Floor 14
Makeen Tower, Al Mawkib St.
Al Zahiya Area
Abu Dhabi, UAE
Mezzanine Floor, Tower 3
Mohammad Thunayyan Al-Ghanem Street, Jibla
Kuwait City, Kuwait
+971 4 3383365
[email protected]
160 Kemp House, City Road
London, EC1V 2NX
United Kingdom
Company Number: 10276574
The website is our proprietary property and all source code, databases, functionality, software, website designs, audio, video, text, photographs, icons and graphics on the website (collectively, the “Content”) are owned or controlled by us or licensed to us, and are protected by copyright laws and various other intellectual property rights. The content and graphics may not be copied, in part or full, without the express permission of DTS Solution LLC (owner) who reserves all rights.
DTS Solution, DTS-Solution.com, the DTS Solution logo, HAWKEYE, FYNSEC, FRONTAL, HAWKEYE CSOC WIKI and Firewall Policy Builder are registered trademarks of DTS Solution, LLC.